Difference between revisions of "MIDI"
From CPCWiki - THE Amstrad CPC encyclopedia!
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
* [[Music Machine]] (Sampling/Playback/MIDI) (RAM Electronics) | * [[Music Machine]] (Sampling/Playback/MIDI) (RAM Electronics) | ||
* [[Silicon Systems MIDI Interface]] | * [[Silicon Systems MIDI Interface]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == MIDI software for the CPC == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Foundation Multi-Track Step Time Sequencer]] (Foundation Software) | ||
| + | * [[EMR Miditrack Performer]] (ElectroMusic Research) | ||
== Weblinks == | == Weblinks == | ||
| Line 34: | Line 39: | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIDI_1.0 - wikipedia on MIDI 1.0 | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIDI_1.0 - wikipedia on MIDI 1.0 | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musical_Instrument_Digital_Interface - wikipedia on MIDI in general | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musical_Instrument_Digital_Interface - wikipedia on MIDI in general | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Peripherals]] [[Category:Music_and_sound]] | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 8 March 2012
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI)
Contents
Software Protocol
Basicall transmits commands like key on, key off, plus pitch/volume parameters.
Write more...
Hardware Protocol
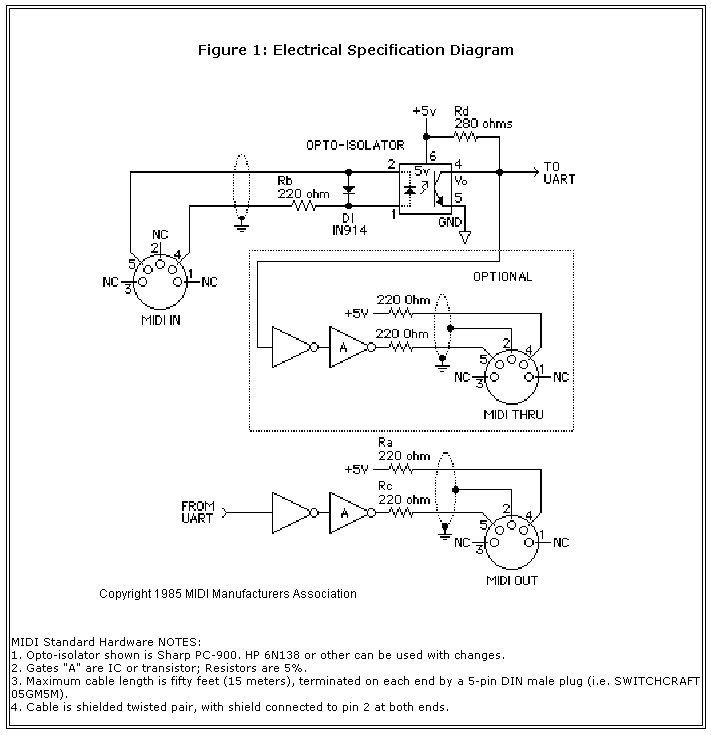
The data is transferred at 31250 bits per second, using 8-N-1 format (one start bit, eight data bits, no parity bit, and one stop bit). So far, the MIDI protocol is much similar to RS232, and many MIDI interfaces do actually use standard "RS232" UART chips. Differences to RS232 are:
- The signals are transmitted as TTL levels (0V and 5V) (unlike +/-12V on RS232) with 5V reference voltage (unlike 0V on RS232)
- The receiver should pass the TTL signal through an Opto-Isolator
- The 31250 Hz baudrate isn't a standard RS232 rate
- MIDI is one-directional (MIDI OUT implements only TX, no RX, and MIDI IN implements only RX, no TX)
- There are no control signals like CTS/RTS/DSR/DTR used
Schematic
MIDI Interfaces for the CPC
- DHCP MIDI Interface (DHCP Electronics)
- EMR MIDI Interface (MIDI) (ElectroMusic Research)
- Music Machine (Sampling/Playback/MIDI) (RAM Electronics)
- Silicon Systems MIDI Interface
MIDI software for the CPC
- Foundation Multi-Track Step Time Sequencer (Foundation Software)
- EMR Miditrack Performer (ElectroMusic Research)
Weblinks
- http://www.midi.org/ - MIDI Manufacturers Association (MMA)
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIDI_1.0 - wikipedia on MIDI 1.0
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musical_Instrument_Digital_Interface - wikipedia on MIDI in general