Difference between revisions of "Connector:Expansion port"
From CPCWiki - THE Amstrad CPC encyclopedia!
m (→Amstrad PCW: typo) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== CPC Expansion Port == | == CPC Expansion Port == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ExpansionPortEdge.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ExpansionPortPlus.png]] | ||
EXPANSION: 50 way Delta range. | EXPANSION: 50 way Delta range. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 34: | ||
== KC Compact Expansion Port == | == KC Compact Expansion Port == | ||
| − | 58pin, special-type | + | |
| + | The [[KC Compact]] has 58pin, special-type connector | ||
1B +12V (20mA max) 29B ............................. 1B | 1B +12V (20mA max) 29B ............................. 1B | ||
1A +20V 29A ............................. 1A | 1A +20V 29A ............................. 1A | ||
| Line 44: | Line 49: | ||
29B Printer /Strobe ; | 29B Printer /Strobe ; | ||
29A Printer Bit6 ;/ | 29A Printer Bit6 ;/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Expansion Port on Aleste 520EX Expansion Port == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[Aleste 520EX]] has a 62pin, male edge connector. | ||
| + | A1..A25 Same as <odd> CPC Pins 1..49 (ie. SOUND, A15, A14, etc.) | ||
| + | B1..B25 Same as <even> CPC Pins 2..50 (except B20=NC, instead /BUSRESET) | ||
| + | A26 MAP14 B26 MAP15 | ||
| + | A27 MAP16 B27 MAP17 A31___________________A1 | ||
| + | A28 MAP18 B28 MAPBLK |___________________| | ||
| + | A29 /INTA B29 /DISP B31 B1 | ||
| + | A30 Agnd B30 /CPU | ||
| + | A31 Aucc B31 HIGH | ||
| + | Most of the extra pins are DMA related. The Aucc/Agnd pins are meant to be smoother voltages then VCC/GND (for use with Audio expansions). | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Amstrad PCW == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Amstrad PCW has a 50-pin Expansion port, too. But its pin-outs are entirely different as on CPC. | ||
| + | * [[Amstrad PCW Expansion Port]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Signal Descriptions== | ||
| + | This information was originally available here: http://www.retroisle.com/amstrad/cpc/Technical/Hardware/ExpansionPorts.php | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The signals are listed in alphabetical order. Signals which have a "/" prefix are "active-low". | ||
| + | |||
| + | More information for signals which are inputs to the CPU or outputs from the CPU can be found by reading other documents or datasheets about the Z80 CPU. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * +5V (5V power) The CPC power output is not able to supply many peripherals. This power output should be used to power IC's and used as a signal reference only. | ||
| + | * φ 4MHz Clock | ||
| + | * A15-A0 (Address bus; Output from CPU). A15-A0 form a 16-bit address. A15-A0 are used to specify a memory address or an I/O address. | ||
| + | * /BUSAK (Bus Acknowledge; Output from CPU). When /BUSAK="0" the CPU is signalling that control of the address bus, data bus and output signals has been released, and the device can take control. | ||
| + | * /BUS RESET (Bus Reset; Input to PIO/CPU) Acts similarly to /RESET but also resets the PIO chip. | ||
| + | * /BUSRQ (Bus Request; Input to CPU). When /BUSRQ="0" a device is requesting control of the address bus, data bus and the CPU's output signals. At the end of the current instruction cycle, the CPU will issue a Bus Acknowledge. | ||
| + | * CURSOR (Cursor; Output from CRTC). When CURSOR="1" the CRTC is displaying the cursor. | ||
| + | * D7-D0 (Data bus; Input to CPU/Output from CPU). D7-D0 form 8-bit data. In a I/O operation, D7-D0 are used to transfer data to/from a I/O device. In a memory operation, D7-D0 are used to transfer data to/from memory. In an interrupt request operation, D7-D0 are used to specify part of an interrupt response vector. | ||
| + | * /EXP (Expansion device connected; Input to PPI). The function of this signal can be used by a device to signal it's presence, it does this by setting this signal to "0". This signal is connected to bit 5 of PPI port B. This signal can be reprogrammed as input or output using the PPI, and can therefore be used as a general purpose input/output. | ||
| + | * Gnd (Signal Ground). Signal Ground. This can be used as a signal reference and as the Gnd connection to IC's. | ||
| + | * /HALT (Halt; Output from CPU). When /HALT="0" the CPU has executed a "HALT" instruction. The CPU will execute "NOP" instructions until a interrupt request is received and interrupts are not masked. | ||
| + | * /INT (Interrupt Request; Input to CPU). This is the maskable interrupt input to the CPU. When /INT="0" a interrupt request is signalled to the CPU. In the CPC, the interrupts are generated by the Gate-Array. In the CPC+, the interrupts are generated by the ASIC. In the KC Compact, the interrupts are generated by the Z8536 CIO. | ||
| + | ** If interrupts are masked, the interrupt request is ignored. | ||
| + | ** If interrupts are not masked, the interrupt request will be acknowledged. | ||
| + | * /IORQ (Input/Output Request; Output from CPU). When /IORQ="0" there are two possible functions: | ||
| + | ** Interrupt acknowledge: /M1="0". The interrupt acknowledge function is used to indicate that the interrupting device can put a interrupt vector into D7-D0. | ||
| + | ** I/O operation (read or write): /M1="1", /WR="0" OR /RD="0". The I/O operation is used to read from/write to a I/O device. When the CPU is performing a I/O operation, A15-A0 will contain the I/O address. | ||
| + | *** If /RD is "0" then the operation is reading from a I/O device. D7-D0 will contain data read from the selected device. | ||
| + | *** If /WR is "0" then the operation is writing to a I/O device. D7-D0 contain data to write to the selected device. | ||
| + | * L.PEN (Light Pen trigger; Input to CRTC). A low-to-high ("0" to "1") transition on this signal will cause the CRTC to store the current memory address (CRTC MA signal) it has generated. The CRTC memory address can be used to calculate the position of a light-pen/light-gun on the screen. | ||
| + | * /M1 (Machine cycle one; Output from CPU). When /M1="0" there are two possible functions: | ||
| + | ** Interrupt acknowledge: /IORQ="0" | ||
| + | ** CPU is fetching the op-code part of an instruction: /MREQ="0" and /IORQ="1" | ||
| + | * /MREQ (Memory Request; Output from CPU). When /MREQ="0" the CPU is performing a memory operation. A15-A0 contain the memory address. | ||
| + | ** If /RD is "0" then the operation is reading from memory. D7-D0 will contain data read from the memory. | ||
| + | ** If /WR is "0" then the operation is writing to memory. D7-D0 contain data to write to the memory. | ||
| + | * /NMI (Non-Maskable Interrupt; Input to CPU). When there is a negative-edge on this signal (signal changes from "1" to "0"), this will force the CPU to execute the non-maskable interrupt service routine at &0066. This interrupt can't be masked and has a higher priority than /INT. | ||
| + | * RAMDIS (Internal RAM Disable; Input to Internal RAM). When RAMDIS="1" the internal RAM of the CPC/CPC+/KC Compact is forced inactive. e.g. a ram-expansion device would use this signal to override the internal RAM selection with the ram on the device. The internal RAM would be forced inactive, and the ram on the ram-expansion would be actived. | ||
| + | * /RAMRD (Ram Read; Output from Gate-Array). When /RAMRD="0" a ram read operation is active. This signal is generated by the Gate-Array. This signal will be "0" when: | ||
| + | ** A15=A14="0" and bit 2 of the Gate-Array ROM configuration register is set to 1. (lower ROM disable) | ||
| + | ** A15=A14="1" and bit 3 of the Gate-Array ROM configuration register is set to 1. (upper ROM disable) | ||
| + | ** A15 is not equal to A14. | ||
| + | * /RD (Read; Output from CPU). When /RD="0" the CPU is performing a read operation. The operations are: | ||
| + | ** Reading from a I/O device: (/IORQ="0", A15-A0 contain I/O address) | ||
| + | ** Reading from memory (/MREQ="0", A15-A0 contain memory address) | ||
| + | * /RESET (Reset; Input to CPU). When /RESET="0" the CPU is held in the reset state. When the reset state is released, the CPU Program Counter (PC) is set to "0" and execution begins resumes from the new PC address. | ||
| + | * /RFSH (Refresh; Output from CPU). When /RFSH="0" and /MREQ="0" this indicates that A6-A0 contain a refresh memory address that can be used to refresh the memory | ||
| + | * ROMDIS (Internal ROM Disable; Input to internal ROM). When ROMDIS="1" the internal ROM of the CPC/CPC+/KC Compact is forced inactive. e.g. a ROM-board device would use this signal to override the ROM selection with a ROM plugged into the device. The internal ROM would be forced inactive, and the selected expansion ROM would be activated. | ||
| + | * /ROMEN (ROM Enable; Output from Gate-Array). When /ROMEN="0" a ROM read operation is active. This signal is generated by the Gate-Array. This signal will be "0" when: | ||
| + | ** A15=A14="0" and bit 2 of the Gate-Array ROM configuration register is set to 0, (lower ROM enable) | ||
| + | ** A15=A14="1" and bit 3 of the Gate-Array ROM configuration register is set to 0. (upper ROM enable) | ||
| + | ** A expansion device (e.g. a ROM-board) can use this signal to activate the selected ROM plugged into the device. | ||
| + | * Sound (Mono Audio; Output from PSG). This is a mono audio signal generated by mixing the 3 PSG audio channels together. | ||
| + | * /WAIT (Ready / Wait; Input to CPU, Output from Gate-Array). When /WAIT="0" this signal is used to delay memory or I/O access by the CPU. This signal is used to force the CPU to access memory or I/O when it is ready. This signal is generated by the Gate-Array. | ||
| + | * /WR (Write; Output from CPU). When /WR="0" the CPU is performing a write operation. The operations are: | ||
| + | ** Writing to a I/O device: (/IORQ="0", A15-A0 contain I/O address) | ||
| + | ** Writing to memory (/MREQ="0", A15-A0 contain memory address) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Peripherals]][[Category:CPC Internal Components]][[Category:CPC Plus]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:53, 29 October 2023
Contents
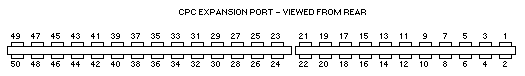
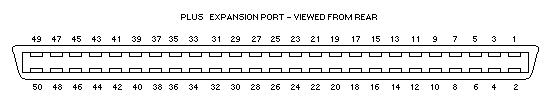
CPC Expansion Port
EXPANSION: 50 way Delta range.
1 Sound 2 GND 3 A15 4 A14 5 A13 6 A12 7 A11 8 A10 9 A9 10 A8 11 A7 12 A6 13 A5 14 A4 15 A3 16 A2 17 A1 18 A0 19 D7 20 D6 21 D5 22 D4 23 D3 24 D2 25 D1 26 D0 27 VCC 28 *MREQ 29 *M1 30 *RFSH 31 *IORQ 32 *RD 33 *WR 34 *HALT 35 *INT 36 *NMI 37 *BUSRQ 38 *BUSAK 39 READY 40 *BRST 41 *RSET 42 *ROMEN 43 ROMDIS 44 *RAMRD 45 RAMDIS 46 CURSOR 47 LPEN 48 *EXP 49 GND 50 CLK4
KC Compact Expansion Port
The KC Compact has 58pin, special-type connector
1B +12V (20mA max) 29B ............................. 1B 1A +20V 29A ............................. 1A 2B Same as CPC Pin1 (SOUND) 2A Same as CPC Pin2 (GND) .. Same as CPC Pin3..48 (see there) 26B Same as CPC Pin49 (GND) 26A Same as CPC Pin50 (4MHz) 27B FBAS Video Output 27A PIO /TEST ;\ 28B Printer Bit1 ; 28A Printer Bit0 ; for TEST mode (remote-network-boot) 29B Printer /Strobe ; 29A Printer Bit6 ;/
Expansion Port on Aleste 520EX Expansion Port
The Aleste 520EX has a 62pin, male edge connector.
A1..A25 Same as <odd> CPC Pins 1..49 (ie. SOUND, A15, A14, etc.) B1..B25 Same as <even> CPC Pins 2..50 (except B20=NC, instead /BUSRESET) A26 MAP14 B26 MAP15 A27 MAP16 B27 MAP17 A31___________________A1 A28 MAP18 B28 MAPBLK |___________________| A29 /INTA B29 /DISP B31 B1 A30 Agnd B30 /CPU A31 Aucc B31 HIGH
Most of the extra pins are DMA related. The Aucc/Agnd pins are meant to be smoother voltages then VCC/GND (for use with Audio expansions).
Amstrad PCW
The Amstrad PCW has a 50-pin Expansion port, too. But its pin-outs are entirely different as on CPC.
Signal Descriptions
This information was originally available here: http://www.retroisle.com/amstrad/cpc/Technical/Hardware/ExpansionPorts.php
The signals are listed in alphabetical order. Signals which have a "/" prefix are "active-low".
More information for signals which are inputs to the CPU or outputs from the CPU can be found by reading other documents or datasheets about the Z80 CPU.
- +5V (5V power) The CPC power output is not able to supply many peripherals. This power output should be used to power IC's and used as a signal reference only.
- φ 4MHz Clock
- A15-A0 (Address bus; Output from CPU). A15-A0 form a 16-bit address. A15-A0 are used to specify a memory address or an I/O address.
- /BUSAK (Bus Acknowledge; Output from CPU). When /BUSAK="0" the CPU is signalling that control of the address bus, data bus and output signals has been released, and the device can take control.
- /BUS RESET (Bus Reset; Input to PIO/CPU) Acts similarly to /RESET but also resets the PIO chip.
- /BUSRQ (Bus Request; Input to CPU). When /BUSRQ="0" a device is requesting control of the address bus, data bus and the CPU's output signals. At the end of the current instruction cycle, the CPU will issue a Bus Acknowledge.
- CURSOR (Cursor; Output from CRTC). When CURSOR="1" the CRTC is displaying the cursor.
- D7-D0 (Data bus; Input to CPU/Output from CPU). D7-D0 form 8-bit data. In a I/O operation, D7-D0 are used to transfer data to/from a I/O device. In a memory operation, D7-D0 are used to transfer data to/from memory. In an interrupt request operation, D7-D0 are used to specify part of an interrupt response vector.
- /EXP (Expansion device connected; Input to PPI). The function of this signal can be used by a device to signal it's presence, it does this by setting this signal to "0". This signal is connected to bit 5 of PPI port B. This signal can be reprogrammed as input or output using the PPI, and can therefore be used as a general purpose input/output.
- Gnd (Signal Ground). Signal Ground. This can be used as a signal reference and as the Gnd connection to IC's.
- /HALT (Halt; Output from CPU). When /HALT="0" the CPU has executed a "HALT" instruction. The CPU will execute "NOP" instructions until a interrupt request is received and interrupts are not masked.
- /INT (Interrupt Request; Input to CPU). This is the maskable interrupt input to the CPU. When /INT="0" a interrupt request is signalled to the CPU. In the CPC, the interrupts are generated by the Gate-Array. In the CPC+, the interrupts are generated by the ASIC. In the KC Compact, the interrupts are generated by the Z8536 CIO.
- If interrupts are masked, the interrupt request is ignored.
- If interrupts are not masked, the interrupt request will be acknowledged.
- /IORQ (Input/Output Request; Output from CPU). When /IORQ="0" there are two possible functions:
- Interrupt acknowledge: /M1="0". The interrupt acknowledge function is used to indicate that the interrupting device can put a interrupt vector into D7-D0.
- I/O operation (read or write): /M1="1", /WR="0" OR /RD="0". The I/O operation is used to read from/write to a I/O device. When the CPU is performing a I/O operation, A15-A0 will contain the I/O address.
- If /RD is "0" then the operation is reading from a I/O device. D7-D0 will contain data read from the selected device.
- If /WR is "0" then the operation is writing to a I/O device. D7-D0 contain data to write to the selected device.
- L.PEN (Light Pen trigger; Input to CRTC). A low-to-high ("0" to "1") transition on this signal will cause the CRTC to store the current memory address (CRTC MA signal) it has generated. The CRTC memory address can be used to calculate the position of a light-pen/light-gun on the screen.
- /M1 (Machine cycle one; Output from CPU). When /M1="0" there are two possible functions:
- Interrupt acknowledge: /IORQ="0"
- CPU is fetching the op-code part of an instruction: /MREQ="0" and /IORQ="1"
- /MREQ (Memory Request; Output from CPU). When /MREQ="0" the CPU is performing a memory operation. A15-A0 contain the memory address.
- If /RD is "0" then the operation is reading from memory. D7-D0 will contain data read from the memory.
- If /WR is "0" then the operation is writing to memory. D7-D0 contain data to write to the memory.
- /NMI (Non-Maskable Interrupt; Input to CPU). When there is a negative-edge on this signal (signal changes from "1" to "0"), this will force the CPU to execute the non-maskable interrupt service routine at &0066. This interrupt can't be masked and has a higher priority than /INT.
- RAMDIS (Internal RAM Disable; Input to Internal RAM). When RAMDIS="1" the internal RAM of the CPC/CPC+/KC Compact is forced inactive. e.g. a ram-expansion device would use this signal to override the internal RAM selection with the ram on the device. The internal RAM would be forced inactive, and the ram on the ram-expansion would be actived.
- /RAMRD (Ram Read; Output from Gate-Array). When /RAMRD="0" a ram read operation is active. This signal is generated by the Gate-Array. This signal will be "0" when:
- A15=A14="0" and bit 2 of the Gate-Array ROM configuration register is set to 1. (lower ROM disable)
- A15=A14="1" and bit 3 of the Gate-Array ROM configuration register is set to 1. (upper ROM disable)
- A15 is not equal to A14.
- /RD (Read; Output from CPU). When /RD="0" the CPU is performing a read operation. The operations are:
- Reading from a I/O device: (/IORQ="0", A15-A0 contain I/O address)
- Reading from memory (/MREQ="0", A15-A0 contain memory address)
- /RESET (Reset; Input to CPU). When /RESET="0" the CPU is held in the reset state. When the reset state is released, the CPU Program Counter (PC) is set to "0" and execution begins resumes from the new PC address.
- /RFSH (Refresh; Output from CPU). When /RFSH="0" and /MREQ="0" this indicates that A6-A0 contain a refresh memory address that can be used to refresh the memory
- ROMDIS (Internal ROM Disable; Input to internal ROM). When ROMDIS="1" the internal ROM of the CPC/CPC+/KC Compact is forced inactive. e.g. a ROM-board device would use this signal to override the ROM selection with a ROM plugged into the device. The internal ROM would be forced inactive, and the selected expansion ROM would be activated.
- /ROMEN (ROM Enable; Output from Gate-Array). When /ROMEN="0" a ROM read operation is active. This signal is generated by the Gate-Array. This signal will be "0" when:
- A15=A14="0" and bit 2 of the Gate-Array ROM configuration register is set to 0, (lower ROM enable)
- A15=A14="1" and bit 3 of the Gate-Array ROM configuration register is set to 0. (upper ROM enable)
- A expansion device (e.g. a ROM-board) can use this signal to activate the selected ROM plugged into the device.
- Sound (Mono Audio; Output from PSG). This is a mono audio signal generated by mixing the 3 PSG audio channels together.
- /WAIT (Ready / Wait; Input to CPU, Output from Gate-Array). When /WAIT="0" this signal is used to delay memory or I/O access by the CPU. This signal is used to force the CPU to access memory or I/O when it is ready. This signal is generated by the Gate-Array.
- /WR (Write; Output from CPU). When /WR="0" the CPU is performing a write operation. The operations are:
- Writing to a I/O device: (/IORQ="0", A15-A0 contain I/O address)
- Writing to memory (/MREQ="0", A15-A0 contain memory address)