Difference between revisions of "3??┬?" & 5??┬?" Disk Drives"
(ŌåÆŌĆÄNotes) |
m (3 1/2" & 5 1/4" Disk Drives moved to 3┬Į" & 5┬╝" Disk Drives: Formal correctness. The easier to type link will still be redirected.) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Besides the "big" brands' disk drives for the Amstrad CPC, there were also user solutions and garage company made disk drives for the Amstrad CPC. | Besides the "big" brands' disk drives for the Amstrad CPC, there were also user solutions and garage company made disk drives for the Amstrad CPC. | ||
| ŌłÆ | + | These usually came without controller and own DOS, so in order to use the full capacity of such drives, you had to replace the built-in AMSDOS with a DOS like ParaDOS or a patched AMSDOS. | |
| ŌłÆ | These usually came without | + | But even without a special DOS taking use of the higher capacity, the use of such drives made sense, as media were much cheaper than 3" media. |
| ŌłÆ | + | Today, with supplies of 3" disks draining and company solutions no longer being produced, a self-made 3┬Į" disk drive is the perfect supplement for every CPC user, especially as it makes the data exchange between CPC and PC much easier. | |
| ŌłÆ | But even without a special DOS taking use of the higher capacity | + | |
| ŌłÆ | + | ||
| ŌłÆ | Today, with supplies of 3" disks draining and company solutions no longer being produced, a self-made | + | |
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| ŌłÆ | * | + | * '''Whereever possible, the wire numbers from the PC standard were used!''' (See the article about the connector for the reason why: [[Connector:2nd disc drive (CPC664, CPC6128, CPC6128+)]] |
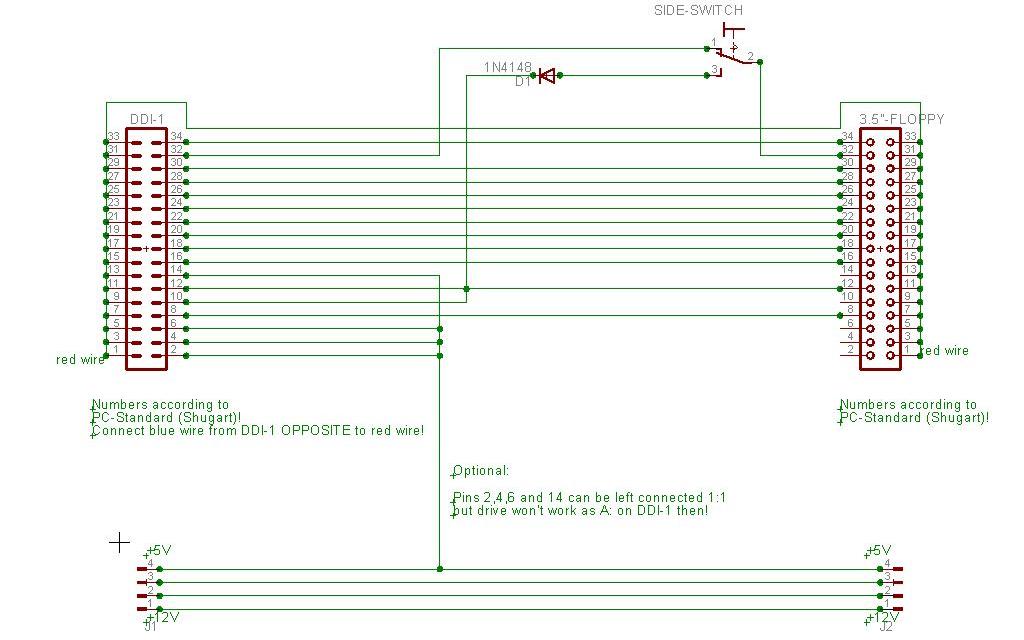
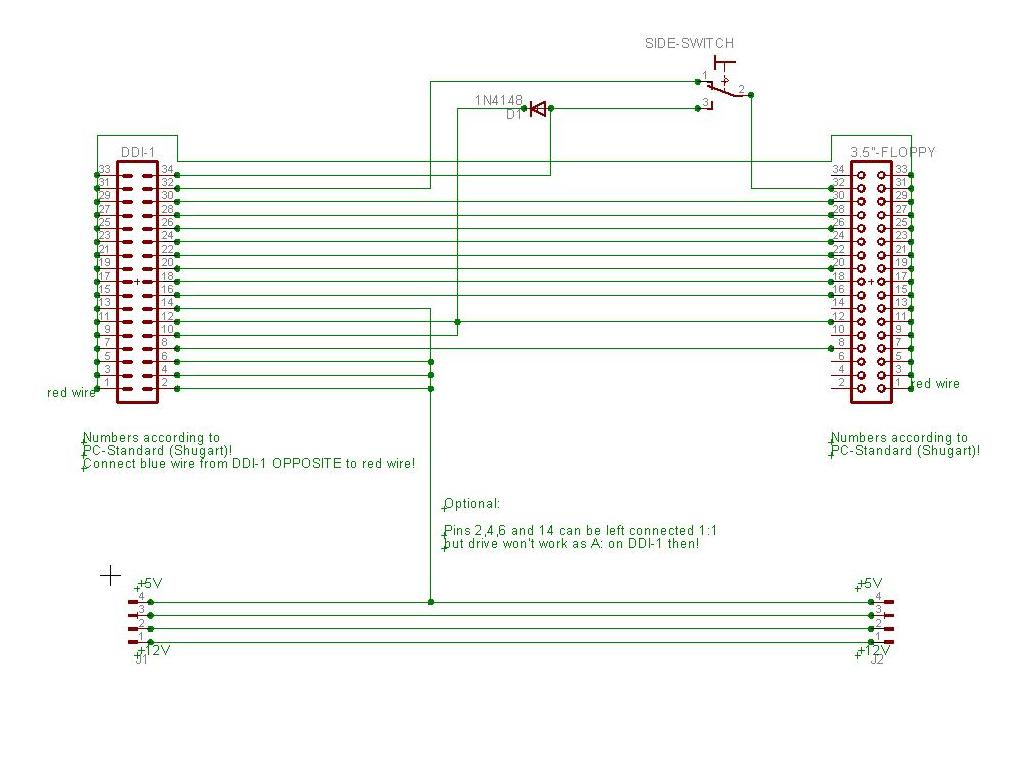
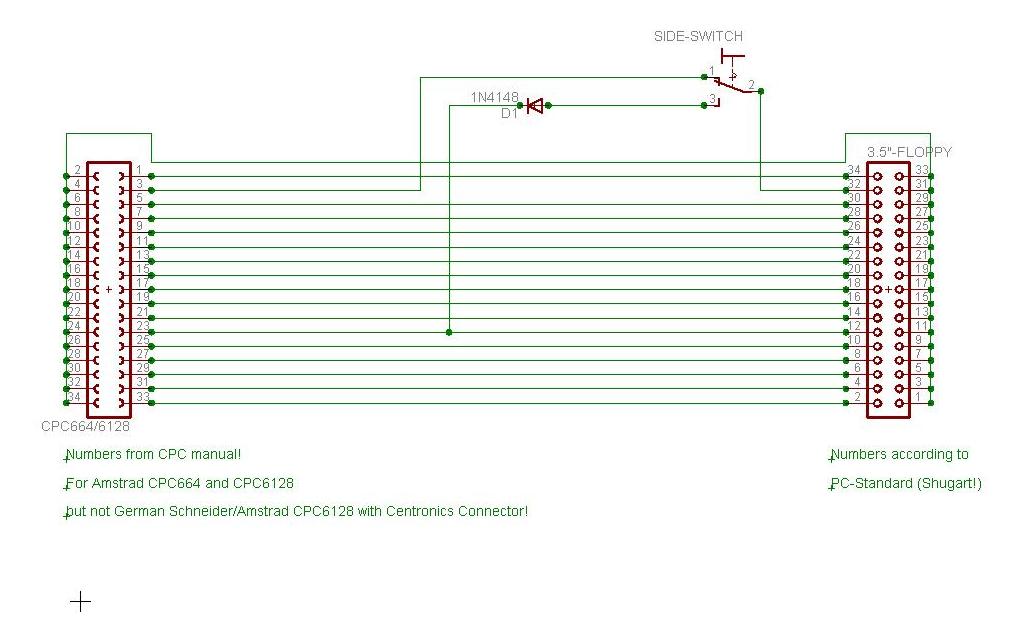
| ŌłÆ | * | + | * These schematics differ from most existing schematics on the web in that way, that they don't use GND to pull signals active low, but the /DRIVE SELECT line via diode. This ensures that the other drive on the bus doesn't become influenced. You can solder the wire containing the diode directly (without the diode) to a GND-wire and you will get the same as described in other tutorials but the side switch and - if applicable - the signal RDY will also be in effect for the other disk drive then. We will refer to this as "permanent" (signal is active all time/for all drives) vs. "semi-permanent" (signal is active while accessing the specific drive only). |
| ŌłÆ | + | ||
| ŌłÆ | + | ||
| ŌłÆ | * | + | * The universal solution connects a 3" or 3┬Į" disk drive to any CPC with disk controller |
| + | ** You can even use Part A for connecting a 3" disk drive to a CPC664/CPC6128/CPC6128plus and Part Bx for connecting a 3┬Į" disk drive to a CPC464 with DDI-1 at the same time | ||
| + | ** Part Bx, which is also the full cable for the CPC464 with DDI-1, can even be used to connect the PC drive as A: on the DDI-1, though this doesn't work with all drives, probably due to the drive's RDY-conditions during power up not being met by the CPC-controller (Old TEAC drives with lots of jumpers are known to work, while some other brands won't, although they have a RDY-signal sufficient for the operation as drive B:. In such cases you will either need to play with the drives MOTOR ON jumpers, get a "better" drive or a (semi-)permanent RDY even for drives with own RDY.) | ||
| ŌłÆ | * | + | * Although schematics for drives without own RDY-Signal are included, it is highly recommended to use drives with RDY to ensure maximum compatibility. However, drives that can simply be jumpered for a proper RDY-signal aren't made any more and can probably only be bought used. Though, some drives that are still be sold or were still be sold recently can be [[Modify PC floppy drives|modified]] for a RDY-signal. Keep the limitations from the previous note in mind when using such a drive as A:. This especially applies to modified (rather than jumpered) drives. |
| ŌłÆ | * Hints for fitting cut/squeeze plugs on flat-ribbon cable (Assuming you were building the cable according to the PC wire numbers with red wire = wire 1), connectors seen from back: | + | * Hints for fitting cut/squeeze plugs on flat-ribbon cable (Assuming you were building the cable according to the PC wire numbers with red wire = wire 1), connectors seen from back: |
| ŌłÆ | ** Amstrad | + | ** Schneider/Amstrad CPC6128 with Centronics connector: Red wire showing to the right with two free pins on the right end of the connector (Mainly Schneider, but also the Amstrad CPC6128 sold in Germany. Many of these Schneider CPC6128 were also sold in France) |
| ŌłÆ | + | ** Amstrad CPC664/CPC6128: Red wire showing away from orientation nose inside the connector | |
| ŌłÆ | ** Amstrad CPC6128plus: | + | ** Amstrad CPC6128plus: Red wire showing to the right with three unused pins on the left end of the connector (red wire not connected/overlapping end of connector) |
== Schematics == | == Schematics == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 25: | ||
=== Universal solution (CPC464+DDI-1, CPC664, CPC6128, CPC6128 German and CPC6128plus) === | === Universal solution (CPC464+DDI-1, CPC664, CPC6128, CPC6128 German and CPC6128plus) === | ||
| ŌłÆ | ==== Part A: | + | ==== Part A: Replacement cable for original Amstrad/Schneider FD-1 ==== |
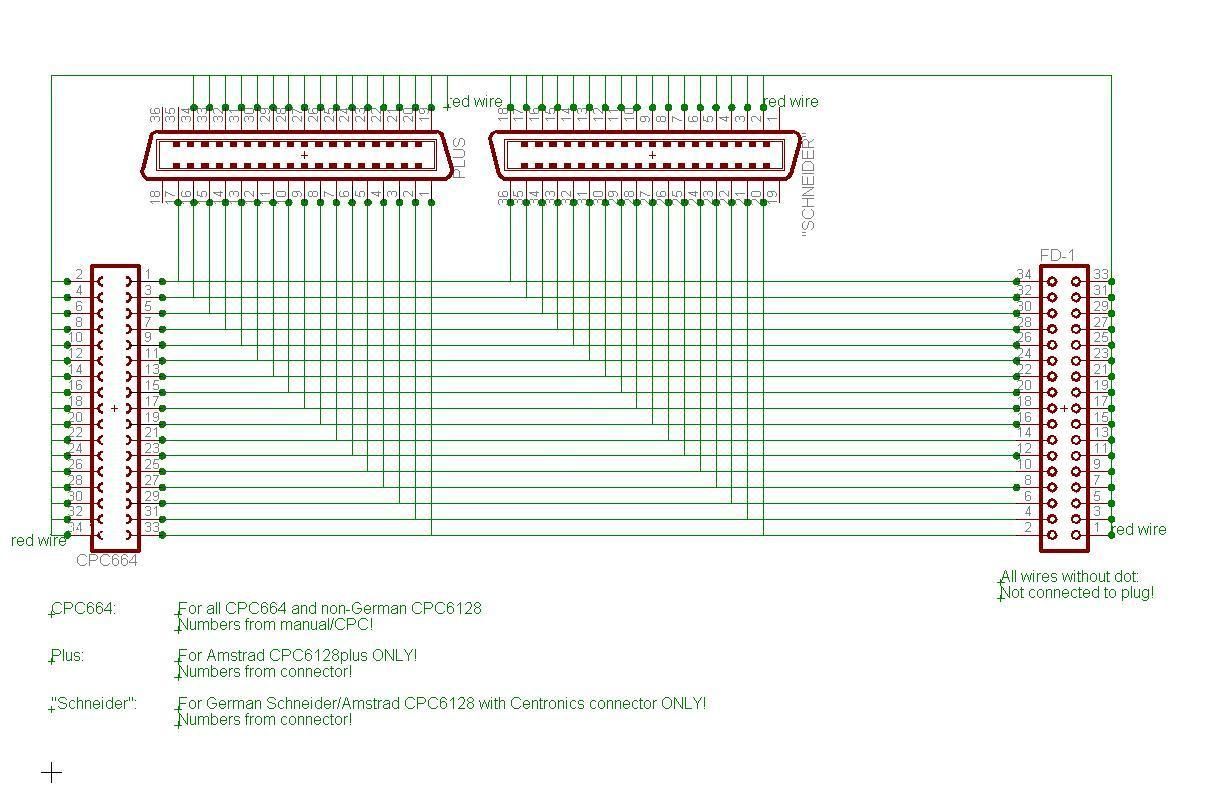
[[Image:Universal FD-1.jpg|frame|none|Identical to the cable for the FD-1 except that it is for the CPC664, CPC6128 and CPC6128plus at the same time]] | [[Image:Universal FD-1.jpg|frame|none|Identical to the cable for the FD-1 except that it is for the CPC664, CPC6128 and CPC6128plus at the same time]] | ||
| Line 74: | Line 71: | ||
[[Image:CPC6128plus - 3.5 wo RDY.jpg|frame|none|Schematics for PC disk drives without own READY signal on an Amstrad CPC6128plus]] | [[Image:CPC6128plus - 3.5 wo RDY.jpg|frame|none|Schematics for PC disk drives without own READY signal on an Amstrad CPC6128plus]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
== Garage companies that sold disc drives == | == Garage companies that sold disc drives == | ||
* [[Frank Strauss Elektronik|Frank Straus 5 1/4" Drive]] | * [[Frank Strauss Elektronik|Frank Straus 5 1/4" Drive]] | ||
| ŌłÆ | * G+L Electronic ( | + | * G+L Electronic (3┬Į" and 5┬╝" disk drives) |
[[Category:Hardware]] [[Category:Peripherals]] | [[Category:Hardware]] [[Category:Peripherals]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:12, 4 November 2007
Besides the "big" brands' disk drives for the Amstrad CPC, there were also user solutions and garage company made disk drives for the Amstrad CPC. These usually came without controller and own DOS, so in order to use the full capacity of such drives, you had to replace the built-in AMSDOS with a DOS like ParaDOS or a patched AMSDOS. But even without a special DOS taking use of the higher capacity, the use of such drives made sense, as media were much cheaper than 3" media. Today, with supplies of 3" disks draining and company solutions no longer being produced, a self-made 3┬Į" disk drive is the perfect supplement for every CPC user, especially as it makes the data exchange between CPC and PC much easier.
Contents
- 1 Notes
- 2 Schematics
- 3 Garage companies that sold disc drives
Notes
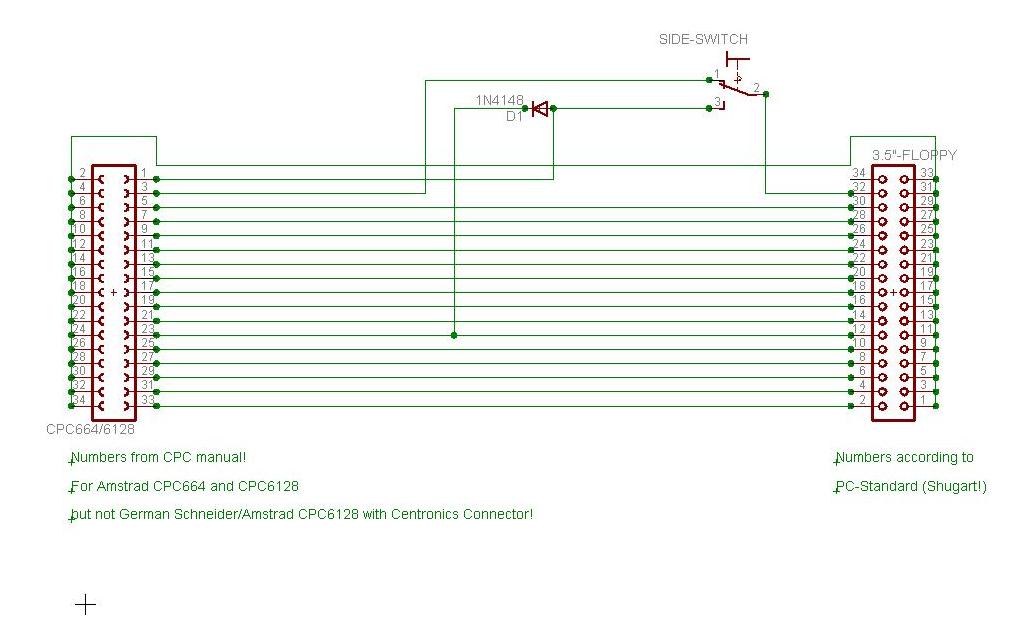
- Whereever possible, the wire numbers from the PC standard were used! (See the article about the connector for the reason why: Connector:2nd disc drive (CPC664, CPC6128, CPC6128+)
- These schematics differ from most existing schematics on the web in that way, that they don't use GND to pull signals active low, but the /DRIVE SELECT line via diode. This ensures that the other drive on the bus doesn't become influenced. You can solder the wire containing the diode directly (without the diode) to a GND-wire and you will get the same as described in other tutorials but the side switch and - if applicable - the signal RDY will also be in effect for the other disk drive then. We will refer to this as "permanent" (signal is active all time/for all drives) vs. "semi-permanent" (signal is active while accessing the specific drive only).
- The universal solution connects a 3" or 3┬Į" disk drive to any CPC with disk controller
- You can even use Part A for connecting a 3" disk drive to a CPC664/CPC6128/CPC6128plus and Part Bx for connecting a 3┬Į" disk drive to a CPC464 with DDI-1 at the same time
- Part Bx, which is also the full cable for the CPC464 with DDI-1, can even be used to connect the PC drive as A: on the DDI-1, though this doesn't work with all drives, probably due to the drive's RDY-conditions during power up not being met by the CPC-controller (Old TEAC drives with lots of jumpers are known to work, while some other brands won't, although they have a RDY-signal sufficient for the operation as drive B:. In such cases you will either need to play with the drives MOTOR ON jumpers, get a "better" drive or a (semi-)permanent RDY even for drives with own RDY.)
- Although schematics for drives without own RDY-Signal are included, it is highly recommended to use drives with RDY to ensure maximum compatibility. However, drives that can simply be jumpered for a proper RDY-signal aren't made any more and can probably only be bought used. Though, some drives that are still be sold or were still be sold recently can be modified for a RDY-signal. Keep the limitations from the previous note in mind when using such a drive as A:. This especially applies to modified (rather than jumpered) drives.
- Hints for fitting cut/squeeze plugs on flat-ribbon cable (Assuming you were building the cable according to the PC wire numbers with red wire = wire 1), connectors seen from back:
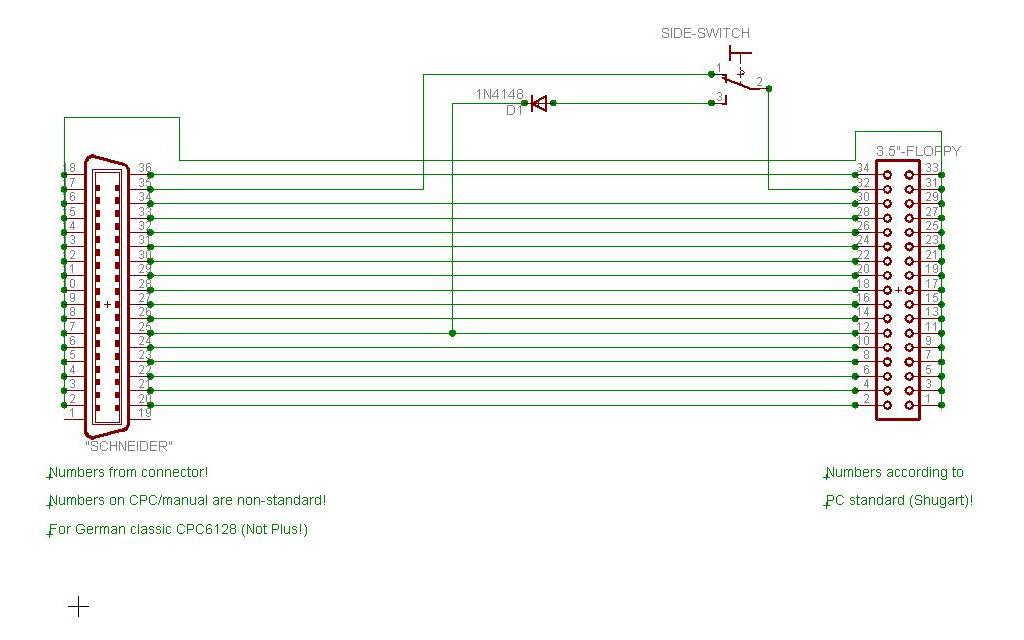
- Schneider/Amstrad CPC6128 with Centronics connector: Red wire showing to the right with two free pins on the right end of the connector (Mainly Schneider, but also the Amstrad CPC6128 sold in Germany. Many of these Schneider CPC6128 were also sold in France)
- Amstrad CPC664/CPC6128: Red wire showing away from orientation nose inside the connector
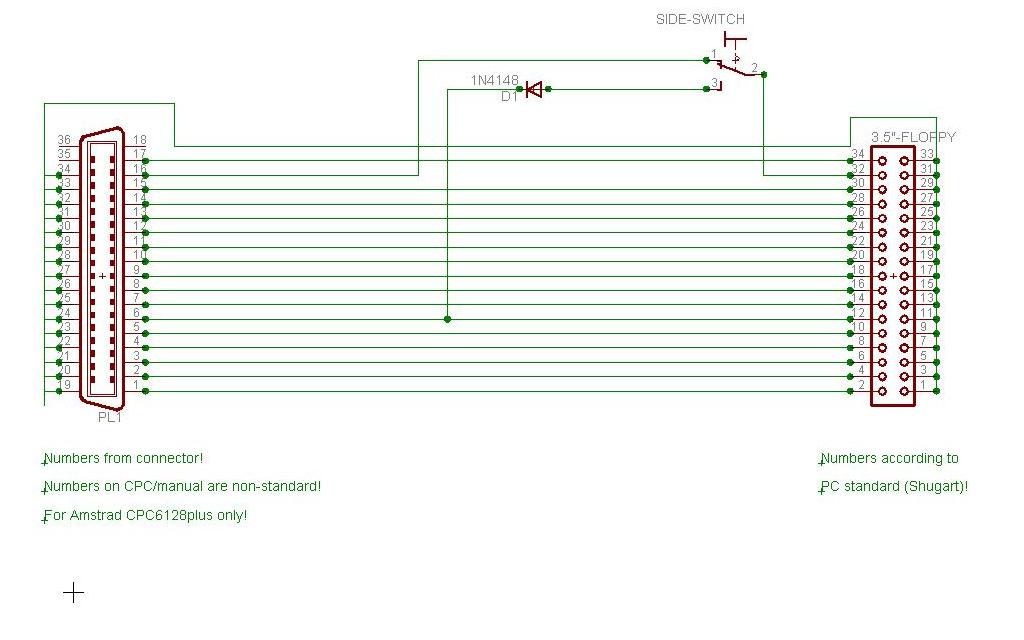
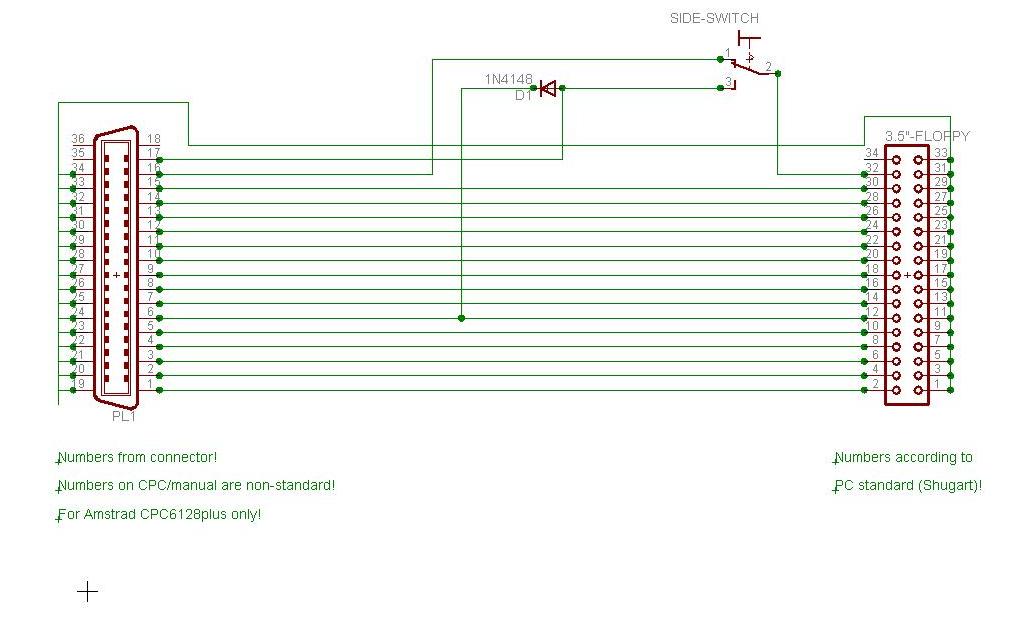
- Amstrad CPC6128plus: Red wire showing to the right with three unused pins on the left end of the connector (red wire not connected/overlapping end of connector)
Schematics
Universal solution (CPC464+DDI-1, CPC664, CPC6128, CPC6128 German and CPC6128plus)
Part A: Replacement cable for original Amstrad/Schneider FD-1
Part B1: Makes a PC disk drive with RDY behave like a DDI-1
Part B2: Makes a PC disk drive without RDY behave like a DDI-1
Amstrad/Schneider CPC464 with DDI-1
See Part B1 or Part B2 as shown in sections 2.1.2 or 2.1.3 accordingly.
Amstrad/Schneider CPC664/CPC6128 (Not German CPC6128s!)
Drive has RDY-signal
Drive doesn't have RDY-signal
Schneider/Amstrad CPC6128 (German models and grey imports from Germany only!)
Drive has RDY-signal
Drive doesn't have RDY-signal
Amstrad CPC6128plus
Drive has RDY-signal
Drive doesn't have RDY-signal
Garage companies that sold disc drives
- Frank Straus 5 1/4" Drive
- G+L Electronic (3┬Į" and 5┬╝" disk drives)