|
|
| (20 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
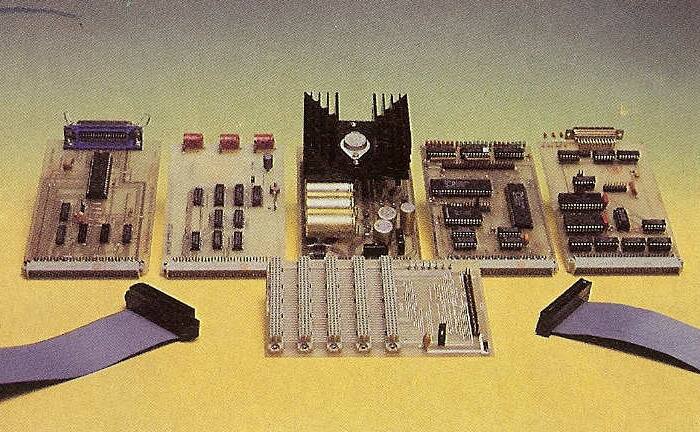
| − | The [[Schneiderware]] series consists of several DIY projects which have been released in german magazine [[CPC Schneider International]] published by [[DMV]]. The name "Schneiderware" was probably choosen due to its double meaning ("CPC Hardware" in computer language, or "specially fitted clothing" in german language). Aside from building the hardware on one's own, one could also order printed circuit boards, either fully assembled, or plain PCBs without components. | + | The [[Schneiderware]] series consists of several DIY projects which have been released 1986-1987 in german magazine [[CPC Schneider International]] published by [[DMV]]. The name "Schneiderware" was probably choosen due to its double meaning ("CPC Hardware" in computer language, or "designer clothing" in german language). Aside from building the hardware on one's own, one could also order printed circuit boards, either fully assembled, or plain PCBs without components. |
| | | | |
| | The various boards are having special connectors, intended to be mounted on the "Basisplatine" (some kind of a motherboard with [[ECB Bus]] sockets) which allows to connect up to five Schneiderware boards to the CPCs Expansion Port; with some small modifications one could also connect the boards directly to the Expansion Port (the motherboard is merely an Y-cable-like adaptor without electrical components, so one doesn't really need it). | | The various boards are having special connectors, intended to be mounted on the "Basisplatine" (some kind of a motherboard with [[ECB Bus]] sockets) which allows to connect up to five Schneiderware boards to the CPCs Expansion Port; with some small modifications one could also connect the boards directly to the Expansion Port (the motherboard is merely an Y-cable-like adaptor without electrical components, so one doesn't really need it). |
| | | | |
| − | * [[Schneiderware Introduction|Schneiderware #1 Introduction (Theory)]] (6/1986, pages 62-67) | + | * [[Schneiderware Introduction|Schneiderware #1 Introduction (Theory)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware Basisplatine|Schneiderware #2a Basisplatine (Motherboard)]] (7/1986, pages 60-67) | + | * [[Schneiderware Basisplatine|Schneiderware #2a Basisplatine (Motherboard)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware Centronics Port|Schneiderware #2b Centronics (Printer Port)]] (7/1986, pages 60-67) | + | * [[Schneiderware Centronics Port|Schneiderware #2b Centronics (Printer Port)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware V/24 Interface|Schneiderware #3 V/24 (RS232 Interface)]] (8/1986, pages 70-77) | + | * [[Schneiderware V/24 Interface|Schneiderware #3 V/24 (RS232 Interface)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware Power Supply|Schneiderware #4 Netzteil (Power Supply)]] (9/1986, pages 78-83) | + | * [[Schneiderware Power Supply|Schneiderware #4 Netzteil (Power Supply)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware Real Time Clock|Schneiderware #5 Echtzeituht (Real Time Clock)]] (10/1986, pages 78-85) | + | * [[Schneiderware Real Time Clock|Schneiderware #5 Echtzeituhr (Real Time Clock)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware Uni-PIO|Schneiderware #6 Uni-PIO (48 I/O lines)]] (12/1986, pages 124-130) | + | * [[Schneiderware Uni-PIO|Schneiderware #6 Uni-PIO (48 I/O lines)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware Analog Converter|Schneiderware #7 A/D and D/A Converter]] (3/1987, pages 32-45) | + | * [[Schneiderware Analog Converter|Schneiderware #7 Analog Converter (8 analog inputs, 2 analog outputs)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware Pseudo ROM|Schneiderware #8 Pseudo ROM (SRAM and EPROM mapped as ROM)]] (4/1987, pages 26-34) (plus corrections in 5/1987, pages 32-34) | + | * [[Schneiderware Pseudo ROM|Schneiderware #8 Pseudo ROM (SRAM and EPROM mapped as ROM)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware EPROM Burner|Schneiderware #9 Eprommer (EPROM Burner)]] (6/1987, pages 122-131) | + | * [[Schneiderware EPROM Burner|Schneiderware #9 Eprommer (EPROM Burner)]] |
| − | * [[Schneiderware Notes|Schneiderware Nachlese (Notes)]] (11/1987, pages 97-99)
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | ----
| + | A summary of the I/O ports, Schematics, Photos, and all scanned articles can be found here: |
| | + | * [[Schneiderware Summary]] |
| | | | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 06/1986, Page 062-067, Schneiderware #1 Introduction (Theory)
| + | '''Note''' - Along with the Schneiderware series, there has been also a "[[CPC Schneider International]] 02/1987, Page ??-??, MIDI Interface" (advertised together with the Schneiderware PCBs, but not part of the Schneiderware series). |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 07/1986, Page 060-067, Schneiderware #2 Basisplatine (Motherboard) & Centronics (Printer Port)
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 08/1986, Page 070-077, Schneiderware #3 V/24 (RS232 Interface)
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 09/1986, Page 078-083, Schneiderware #4 Netzteil (Power Supply)
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 10/1986, Page 078-085, Schneiderware #5 Echtzeituhr (Real Time Clock)
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 12/1986, Page 124-130, Schneiderware #6 Uni-PIO (48 I/O lines)
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 01/1987, Page 144, Schneiderware Advert
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 02/1987, Page ??-??, 7 MIDI Interface (not part of the Schneiderware series)
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 03/1987, Page 032-045, Schneiderware #7 A/D and D/A converter
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 04/1987, Page 026-034, Schneiderware #8 Eprom/RAM (EPROM and battery-backed SRAM; both mapped as expansion ROM)
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 05/1987, Page 032-034, Schneiderware #8 Eprom/RAM (Notes/Corrections)
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 06/1987, Page 122-131, Schneiderware #9 Eprommer (EPROM Burner)
| + | |
| − | * [[CPC Schneider International]] 11/1987, Page 097-099, Schneiderware Nachlese (Notes)
| + | |
| − | Notes: The "Centronics" board is yet another [[8bit Printer Ports|8bit Printer Port]] solution (but different than the [[CPCI 8bit Printer Mod|joystick-signal based one]] that was released a few months earlier in the same magazine). The Real Time Clock is somewhat similar to the [[Real Time Clock|CPCI Real Time Clock]] released in a special issue of the same magazine, but not identical (the RTC chip has different pin-outs, and some of it's 4bit registers are working slightly different, the leap-year bits, for example).
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | Databoxes: '''UHR8000''' RTC-RAM-driver in 10-1986 (hex listing, plus [[Hisoft Devpac]] source code) (caution this version uses incorrect I/O addresses FBE1-FBE3), '''UHRC000X''' RTC-ROM-driver in 4-1987 (this version uses correct I/O addresses FBE2-FBE4). Uni-PIO examples in 12-1986 (=only a few basic lines). There seem to be no Centronics and V/24 drivers included in databoxes.
| + | ---- |
| − | | + | |
| − | == I/O Ports ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | {|{{Prettytable|width: 700px; font-size: 2em;}}
| + | |
| − | |Address (default) || Address (alternate) || Usage
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |DFxxh || N/A || Schneiderware RAM/EPROM - Expansion ROM bank number (W)<br>Battery-backed SRAM and/or EPROM are selected when the bank-number matches the jumper-selected values; the memory is then mapped to C000h..FFFFh (in case of READing one must also enable upper ROM via Gate Array). The bank number decoding is a bit strange:
| + | |
| − | * EPROM/Read bank: All 8 bits decoded (bank 00h..FFh)
| + | |
| − | * SRAM/Read bank: Only lower 4 bits decoded (bank X0h..XFh)
| + | |
| − | * SRAM/Write bank: Only lower 4 bits decoded (bank X0h..XFh)
| + | |
| − | The SRAM/Write mode doesn't disable the internal RAM in the CPC, so writes are going both to SRAM and normal RAM at C000-FFFF, that no matter if upper ROM is enabled/disabled via Gate Array; the author recommended to map VRAM to 4000-7FFF via CRTC registers, in order to prevent video dirt during writing.
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8E0h || F8F0h (later redefined to F8E4h) || Schneiderware Centronics 8255 PPI Port A (data)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8E1h || F8F1h (later redefined to F8E5h) || Schneiderware Centronics 8255 PPI Port B (unused)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8E2h || F8F2h (later redefined to F8E6h) || Schneiderware Centronics 8255 PPI Port C (busy/strobe)<br>(bit7=busy, bit6-1=unused, bit0=strobe; strobe is externally inverted)<br>(autolf is wired to GND, all other control/status signals are not connected)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8E3h || F8F3h (later redefined to F8E7h) || Schneiderware Centronics 8255 PPI Control
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8E8h || F8F0h,F8F8h || Schneiderware Uni-PIO 8255 PPI #1 Port A ('''without''' pull-ups, with red LEDs)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8E9h || F8F1h,F8F9h || Schneiderware Uni-PIO 8255 PPI #1 Port B ('''with''' pull-ups and green LEDs)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8EAh || F8F2h,F8FAh || Schneiderware Uni-PIO 8255 PPI #1 Port C (lower 4bit '''without''' pull-ups and red LEDs, upper 4bit '''with''' pull-ups and green LEDs)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8EBh || F8F3h,F8FBh || Schneiderware Uni-PIO 8255 PPI #1 Control
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8ECh || F8F4h,F8FCh || Schneiderware Uni-PIO 8255 PPI #2 Port A (without pull-ups or LEDs)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8EDh || F8F5h,F8FDh || Schneiderware Uni-PIO 8255 PPI #2 Port B (without pull-ups or LEDs)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8EEh || F8F6h,F8FEh || Schneiderware Uni-PIO 8255 PPI #2 Port C (without pull-ups or LEDs)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F8EFh || F8F7h,F8FFh || Schneiderware Uni-PIO 8255 PPI #2 Control
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F9E0h || F9E2h || Schneiderware V/24 8251 USART Data
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F9E1h || F9E3h || Schneiderware V/24 8251 USART Control
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F9ECh || F9E8h || Schneiderware V/24 8253 Timer 0 (TX clock)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F9EDh || F9E9h || Schneiderware V/24 8253 Timer 1 (RX clock)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F9EEh || F9EAh || Schneiderware V/24 8253 Timer 2 (unused)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |F9EFh || F9EBh || Schneiderware V/24 8253 Timer Control<br>Note: Timer clock input is jumper select-able: 2MHz (default), or 1MHz
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAE0h || N/A || Schneiderware Analog Board ADC 0848 A/D Converter (R/W)<br>Read: Get 8bit data from selected channel<br>Write: Select channel & mode; bit0..2=channel (0..7), bit3..4=mode, bit5-7=unused<br>
| + | |
| − | * Mode 0 (or 1) - Differential: Plus=Channel(N), Minus=Channel(N XOR 1)
| + | |
| − | * Mode 2 - Single-Ended: Plus=Channel(N) and Minus=AGND
| + | |
| − | * Mode 3 - Pseudo-Differential: Plus=Channel(N) and Minus=Channel(7)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAE1h || N/A || Schneiderware Analog Board DAC 0832 D/A Converter #1 (W)<br>Write: 8bit data
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAE2h || N/A || Schneiderware Analog Board DAC 0832 D/A Converter #2 (W)<br>Write: 8bit data
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAF0h || N/A || Schneiderware Eprom Burner 8255 PPI #1 Port A (Data, 8bit)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAF1h || N/A || Schneiderware Eprom Burner 8255 PPI #1 Port B (Address LSBs, 8bit)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAF2h || N/A || Schneiderware Eprom Burner 8255 PPI #1 Port C (Address MSBs, 7bit; bit7=unused)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAF3h || N/A || Schneiderware Eprom Burner 8255 PPI #1 Control
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAF4h || N/A || Schneiderware Eprom Burner 8255 PPI #2 Port A (bit0-7=unused)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAF5h || N/A || Schneiderware Eprom Burner 8255 PPI #2 Port B (bit0-5=unused, bit6=Red LED, bit7=Green LED)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAF6h || N/A || Schneiderware Eprom Burner 8255 PPI #2 Port C (programming signals, 8bit)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FAF7h || N/A || Schneiderware Eprom Burner 8255 PPI #2 Control
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FBE2h || BUGGED:FBE1h || Schneiderware RTC index/control (W)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FBE3h || BUGGED:FBE2h || Schneiderware RTC data 4bit (W)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |FBE4h || BUGGED:FBE3h || Schneiderware RTC data 4bit (R)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Schematics ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | <gallery>
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware Basisplatine Pinouts.png|Motherboard
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware Centronics Schematic.png|Centronics
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware Uni-PIO Schematic.png|Uni-PIO
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware RS232 Schematic.png|RS232
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware Power Supply Schematic.png|Power Supply
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware A-D and D-A Converter Schematic.png|DAC/ADC
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware RTC Schematic.png|RTC
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware SRAM and EPROM Schematic.png|SRAM/EPROM
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware EPROM Burner Schematic.png|Eprom Burner
| + | |
| − | </gallery>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Pictures ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | <gallery>
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 2 Basisplatine (component side).jpg |Schneiderware #2<br>Basisplatine (component side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 2 Basisplatine (solder side).jpg |Schneiderware #2<br>Basisplatine (solder side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 2 Centronics (component side).jpg |Schneiderware #2<br>Centronics (component side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 2 Centronics (solder side).jpg |Schneiderware #2<br>Centronics (solder side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 3 V24 (component side).jpg |Schneiderware #3<br>V24 (component side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 3 V24 (solder side).jpg |Schneiderware #3<br>V24 (solder side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 4 Netzteil (component side).jpg |Schneiderware #4<br>Supply/Netzteil (only +12V/-12V components installed)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 4 Netzteil (solder side).jpg |Schneiderware #4<br>Supply/Netzteil (solder side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 5 Echtzeituhr (component side).jpg |Schneiderware #5<br>RTC/Echtzeituhr (component side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 5 Echtzeituhr (solder side).jpg |Schneiderware #5<br>RTC/Echtzeituhr (solder side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 6 Uni-PIO (component side).jpg |Schneiderware #6<br>Uni-PIO (component side)
| + | |
| − | File:Schneiderware 6 Uni-PIO (solder side).jpg |Schneiderware #6<br>Uni-PIO (solder side)
| + | |
| − | </gallery>
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | == Datasheets ==
| + | [[Image:Schneiderware Series.jpg]] |
| | | | |
| − | * [[Media:M5832 Datasheet.pdf|M5832 Datasheet]] - Real time clock
| + | [[Category:Peripherals]] |
The various boards are having special connectors, intended to be mounted on the "Basisplatine" (some kind of a motherboard with ECB Bus sockets) which allows to connect up to five Schneiderware boards to the CPCs Expansion Port; with some small modifications one could also connect the boards directly to the Expansion Port (the motherboard is merely an Y-cable-like adaptor without electrical components, so one doesn't really need it).
A summary of the I/O ports, Schematics, Photos, and all scanned articles can be found here: