Difference between revisions of "FutureOS"
m (→Introduction) |
|||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
== Supported Hardware == | == Supported Hardware == | ||
| − | '''8 bit printer ports<br>''' | + | '''8 bit printer ports<br>''' |
*8 bit printer port 6128 Plus | *8 bit printer port 6128 Plus | ||
*8 bit printer port patch ([[8255|PIO]]) | *8 bit printer port patch ([[8255|PIO]]) | ||
| − | '''Drives<br>''' | + | '''Drives<br>''' |
*3" A, B, C and D drives (C, D need hardware patch) | *3" A, B, C and D drives (C, D need hardware patch) | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
*Vortex M1-X | *Vortex M1-X | ||
| − | '''Expansion cards<br>''' | + | '''Expansion cards<br>''' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[SYMBiFACE II|SYMBiFACE II]] | *[[SYMBiFACE II|SYMBiFACE II]] | ||
| − | '''Floppy discs, formats:<br>''' | + | '''Floppy discs, formats:<br>''' |
*Data | *Data | ||
| Line 84: | Line 82: | ||
*Hegetron [[Grafpad II|Grafpad II]] | *Hegetron [[Grafpad II|Grafpad II]] | ||
| − | '''Hard-disc<br>''' | + | '''Hard-disc<br>''' |
| − | *[[Dobbertin Harddisc|Dobbertin HD20]] (72 KB/s data transfer rate) | + | *[[Dobbertin Harddisc|Dobbertin HD20]] (72 KB/s data transfer rate) |
| − | + | ||
| − | '''Joysticks<br>''' | + | '''Joysticks<br>''' |
*Analog Joystick (6128 Plus) | *Analog Joystick (6128 Plus) | ||
| Line 95: | Line 92: | ||
*Digital Joystick 2 | *Digital Joystick 2 | ||
| − | '''Light-Pens<br>''' | + | '''Light-Pens<br>''' |
*[[Dk'tronics Lightpen|Dk'tronics]] | *[[Dk'tronics Lightpen|Dk'tronics]] | ||
| Line 101: | Line 98: | ||
*Lindy | *Lindy | ||
| − | '''Memory expansions<br>''' | + | '''Memory expansions<br>''' |
| − | *[[Dk'tronics memory expansion|Dk'tronics]] 64-512 KB and compatibles ([[Dobbertin Memory Expansion|Dobbertin]], [[SYMBiFACE II|SYMBiFACE II]] | + | *[[Dk'tronics memory expansion|Dk'tronics]] 64-512 KB and compatibles ([[Dobbertin Memory Expansion|Dobbertin]], [[SYMBiFACE II|SYMBiFACE II]], [[Inicron RAM-Box|Inicron]], [[RAM7 2Mb memory expansion|RAM7's RAM expansion]]) |
| − | + | *[[CPC4MB|Jareks 4 MB RAM expansion]] up to 4 MB | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | *[[ | + | |
'''Mouses''' | '''Mouses''' | ||
Revision as of 06:05, 13 January 2009
Contents
Introduction
FutureOS is an operating system for the Amstrad CPC6128, 6128Plus, C-One and T-Rex1. The version for the CPCPlus supports some of its special features. FutureOS is developed by TFM of FutureSoft in Z80 assembler. Its development continues from 1989 up to now (2008). FutureOS allows the user to control the computer with with an icon section and a file section; it can deal with files up to 4 MB big in one piece. It has a dynamic memory management system, which divides RAM into 16 KB blocks. Further it supports a variety of hardware expansions. FutureOS is delivered together with basic utilities in the same ROMs.
Requirements
The core of the OS needs 64 KB ROM. Compatible products are EPROM-cards, the ROM-RAM-BOX, SYMBiFACE II, RAMcard, Jareks Flash-ROM or similar products. If you don't own such a card, you can take a look at FutureOS by using a compatible CPC Emulator (WinCPC, Caprice, WinApe, CPCEmu).
The core of the OS itself is executed directly in (Pseudo-)ROM or EPROM (in four 16 KB blocks). It jumps between the ROMs with the help of a little common area. Therefore the numbers of the four 16 KB ROMs are hardcoded.
FutureOS uses 2 KB (&B800...&BFFF) of the first 64 KB; the rest of the RAM is available to applications. Additional RAM can be reserved for DIRectory buffering. Furthermore the OS uses memory management, file-handling and specialized Low/Mid/High-level routines to access the hardware.
FutureOS can be launched from AmsDOS with the RSX commands |OS or |FDESK. If you use |FDESK you can leave FutureOS and get back to BASIC where you have stopped before - the first 48 KB (not the screen) have been preserved.
FutureOS only runs well on a CPC6128 or 6128plus (not CPC464 or 664), because of their support for RAM configuration C3 (essential for the mouse pointer).
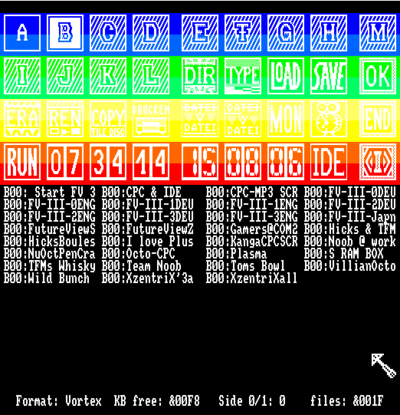
User Interface
The user interface (UI) of FutureOS presents the user with three fixed sections: an icon section (upper half of screen), a file-name display and selection section (lower half of screen) and a message line (bottom). The user can browse through directories of discs and hard-disc partitions. A cursor arrow is used to select devices, functions or files; this cursor arrow can be controlled with a joystick, mouse, trackball, light-pen or the Grafpad II.
Applications can call the UI as a subroutine (the OK icon can be used to return to calling application). The icons are fixed, so the layout remains stable throughout its use.
Files can be viewed on-screen (scroll up and down) or printed. File headers can also be viewed. When typing a text file it is possible to set the number of columns and lines of the window the text is displayed in.
CBM
There is another surface for FutureOS, the command bar menu CBM. It consists of several flexible pull down menus and file selectors. You can easily use CBM for your own programs. Since all programs that use CBM look similar its also easy to use different programs in an intuitive way.
File system
The file system of FutureOS can handle multiple simultaneous floppy disc drives and hard disc partitions. After the selection of a device FutureOS reads and buffers the directory entries of the medium. Integrated utilities like the multi file copy can copy files from physical sources to different physical destinations in one run.
The file system is compatible with the CPCs native data-, file- and format structures (f. e. File header, Disc formats). It is not compatible with native AMSDOS or CP/M programs.
Filenames can use all 256 different characters and user areas from 0 to 254 (except for &E5, which is reserved for deleted files). Unlike Amsdos, a file that is erased under FutureOS is not shifted to user &E5, but is physically removed from the directory. File headers are displayed as AmsDOS files or the icon-like file-header of a FutureOS program. An AmsDOS file header has 128 bytes of which are unused. FutureOS makes use of those unused bytes so that files have a length definition of 24bit and can have a physical RAM select. Therefore a file can be defined to be loaded everywhere in the external RAM. Also a FutureOS file-header can contain a graphical icon, a textual icon or a short description of the file.
Hardware
The OS supports many of the hardware available for the CPC. One of the ambitions of FutureOS is to support all hardware available. Hardware expansions usually need drivers that can be flexibly added to an OS. Contrary to this approach, a goal of FutureOS is to provide a monolithic architecture where all drivers are implemented in a hardcoded way.
- Disc drives and hard discs: FutureOS supports up to eight drives and up to four hard disc partitions. It buffers the directories read from any mass storage device in the expansion RAM.
- Plug and Play: If a hardware expansion is connected to the CPC FutureOS will automatically detect that expansion, initialise it and make it available to the user. The architecture of the OS allows you to add and remove hardware on purpose. The user can switch external hardware on or off in the configuration bytes (use ConfigOS utility).
Supported Hardware
8 bit printer ports
- 8 bit printer port 6128 Plus
- 8 bit printer port patch (PIO)
Drives
- 3" A, B, C and D drives (C, D need hardware patch)
- 3.5" and 5.25" drive
- Atari ST 80 Track DS B-drive
- Dobbertin D-DOS Double drive. Up to four drives 80 track, DS
- Dobbertin X-drive 80 tracks, DS
- Vortex F1-D
- Vortex F1-S
- Vortex F1-X
- Vortex M1-D
- Vortex M1-S
- Vortex M1-X
Expansion cards
Floppy discs, formats:
- Data
- IBM
- System
- Vendor
- Vortex
Graphic Tablet
- Hegetron Grafpad II
Hard-disc
- Dobbertin HD20 (72 KB/s data transfer rate)
Joysticks
- Analog Joystick (6128 Plus)
- Digital Joystick 1
- Digital Joystick 2
Light-Pens
- Dk'tronics
- Happy-Computer
- Lindy
Memory expansions
- Dk'tronics 64-512 KB and compatibles (Dobbertin, SYMBiFACE II, Inicron, RAM7's RAM expansion)
- Jareks 4 MB RAM expansion up to 4 MB
Mouses
- AMX_Mouse
- Atari ST (Schneider Magazin)
- CPC-Mousepack (Reisware)
- CPC-Mousepack 2.0 (Reisware)
- Geos (c64)
- PS/2 mouse of SYMBiFACE II
Real-Time-Clocks
- Dobbertin Smart Watch (at ROM select 15)
- SYMBiFACE II
Trackballs
Utilities
There exist tools like copy, format, verify or directory refreshing. Multiple files can be copied between different physical media in one go.
A small machine monitor is also provided. This monitor provides features like CPU register editing, I/O ports, memory editing and display and manipulation of the ASIC contents (6128 Plus). Memory blocks can be copied or initialised. It is possible to call a routine with defined CPU registers and memory.
Developing for FutureOS
You can developp very freely, even the RST vectors are free usable. Also the second register set of the Z80 is freely usable.
- Z80 Assembler: You can use an assembler for AmsDOS or for CP/M. Switching between AmsDOS and FutureOS is fast and using |FDESK allows to come back to AmsDOS with the first 48 KB or RAM remaining untouched.
- Programming in C for FutureOS: With FIOLIB it also possible to use C as a programming language.
Applications / Demos / Games / Programs
The following programs can be downloaded at the FutureOS homepage, see Weblinks below.
- Captain Future demo
- CBM (pull down menu library)
- Darth Vader demo
- FilmeMacher (movie player)
- FIOLIB (C library)
- Flash ROManager (management of Jareks Flash ROM expansion)
- Fractal demo
- FuturePlayer (MP3 and WAV player)
- FutureView (disc mag)
- Gerelakos (RPG under construction)
- GMSK (sprite converter)
- GSED (Graphic Playground Editor for 2D / 3D games)
- Meg Ryan sample demo
- Return of the Sisters (a Giana Sisters Clone)
- ROManager (management of the Symbiface Pseudo-ROMs)
Conclusion
FutureOS is designed as an OS with fast routines and support for nearly all CPC expansions. It has specialised file handling and memory management capabilities that support programs up to 4 MB. The idea is that development of games, graphic tools, word processors, sound (especially MP3), management of big amounts of data, and programming languages are possible in this environment. At this point, the user can listen to MP3 files, work with graphic, use C programs, watch movies & demos and play games.