Difference between revisions of "Symbos"
(→Web links) |
(→Web links) |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
* [http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/SymbOS spanish Wikipedia article] | * [http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/SymbOS spanish Wikipedia article] | ||
* [http://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/SymbOS italian Wikipedia article] | * [http://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/SymbOS italian Wikipedia article] | ||
| + | * [http://cpcrulez.free.fr/applications_symbos_apply_preview.htm French information on CPCRulez] | ||
| + | * [http://www.wacci.org.uk/magazine/137/137_03.html "New Generation - CPC Windows?"] ([[WACCI]] article by [[CRTC]]) | ||
| + | * [http://www.snakeoillabs.com/2005/10/30/8-bit-guis-eye-candys-not-just-for-the-32-bit/ "8-Bit GUIs - Eye candy’s not just for the 32-bit!"] (Article) | ||
| + | * [http://www.msx.org/forumtopicl6203.html Main thread on MSX.org] | ||
Revision as of 10:06, 6 August 2006
Introduction
Already in the 80's, only few years after the release of the Commodore C64, the legendary GEOS by Berkeley Softworks appeared and set the standard for a windows-based operating system on c64. It was a graphical user-interface (GUI) which was similar to the old desktop of the Apple Macintosh. Powerfull applications were made available for GEOS like GeoWrite (similar to MS-Word) or GeoCalc (similar to MS-Excel). It was incredible, that an 8bit-machine with only 64K was able to realize such an operating system!
On the Amstrad CPC many efforts to build a decent GUI were made as well. In most cases they were just extensions to realize a WIMP (Windows, Icons, Menus and Pointers) environment but weren't true operating systems with their own kernel, memory-management and so on. The CEUS Desktop 2.0 (1990) by Prodatron was just such an extension-system.
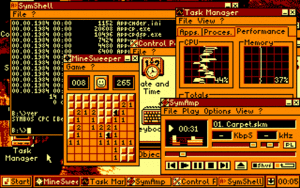
Therefore, the CPC's own OS (in combination with AmsDOS) and CP/M were the only two known OSes for the series, but the question remained: since most CPCs have 128K (most C64 only have 64K), a screen-resolution of 320x200 with 4 colours (C64 only has 2 colours for each 8x8 area in 320x200) and some more advantages, why not have something similar? So the SymbOS-Project was born. SymbOS stands for "SYmbiosis Multitasking Based Operating System". SymbOS is a demonstration of what has been achieved on the CPC: real preemptive multitasking, dynamic memory-management for up to 576K and a totaly MS-Windows-like GUI are the three most important features.
SymbOS started being developed by Prodatron in November 2000 (more details on the development needed)
Features
- Micro kernel
- Maximum amount of supported RAM: 576 KB
- Maximum number of processes 32
- Number of different process priorities 9
- Maximum number of timers 32
- Maximum number of open messages 64
- System manager
- Maximum number of applications 16
- Maximum application core size 63 KB
- Desktop manager
- Maximum number of windows 32
- Maximum number of controls per window 1000
- Maximum possible screen resolution 16.000 x 16.000 pixel
- File manager
- Maximum hard disc size 128 GB
- Maximum file size 2 GB
- Maximum number of devices 8
- Maximum number of open files 8
- Source code
- Source code size (OS Release 1) ~ 30.000 lines
- Source code size (Applications) ~ 34.000 lines
- Total size of the Z80 source code ~ 64.000 lines
Applications
- Applications
- SymCommander (file and disc management)
- SymPlay (video player)
- SymSee (picture viewer)
- SymAmp (jukebox music player)
- Tools and games
- SymSnap (emulator snapshot loader)
- DiskDeDumper (image to disc transfer)
- Speech (voice synthesizer)
- Pocket Calculator (calculator)
- SYMBiFACE II rom manager (rom management for the SYMBiFACE II)
- CPC TREX starter (rom and disc image configuration for the CPC TREX)
- MineSweeper (game)
- System programs
- Control Panel (system configuration)
- Task Manager (system monitor)
- SymShell (command line interface)