Difference between revisions of "A surgical guide to the Amstrad NC"
(→Specifications) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== A Surgical Guide To The Amstrad Notepad Computer == | == A Surgical Guide To The Amstrad Notepad Computer == | ||
| − | This page is based on Hans-Jürgen Böhling's "surgical guide to the Amstrad NC". The original document is avaliabe here [http://home.arcor.de/h.boehling/nc100.htm] ( | + | This page is based on Hans-Jürgen Böhling's "surgical guide to the Amstrad NC". The original document is avaliabe here [https://web.archive.org/web/20141214160211/http://home.arcor.de/h.boehling/nc100.htm] (author's website) or here [[Media:sg-nc100.zip]] (local copy) |
=== Amstrad Notepad Computer - What is it? === | === Amstrad Notepad Computer - What is it? === | ||
| − | The model NC100 is about DIN A4 size with a LCD 8 lines * 80 characters | + | The model [[NC Series|NC100]] is about DIN A4 size with a LCD 8 lines * 80 characters |
screen, nearly full size keyboard, a PCMCIA memory card slot on the right | screen, nearly full size keyboard, a PCMCIA memory card slot on the right | ||
hand side and four coloured keys. The Notepads have standard Centronics | hand side and four coloured keys. The Notepads have standard Centronics | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
Processor : Z80 compatible CMOS | Processor : Z80 compatible CMOS | ||
Operating | Operating | ||
| − | frequency : | + | frequency : 4.606 MHz |
Memory : 64K byte internal | Memory : 64K byte internal | ||
(15K system-, 11K upper-, 38K lower memory) | (15K system-, 11K upper-, 38K lower memory) | ||
Storage : PCMCIA/JEIDA Memory Cards (PC-Cards) Type I | Storage : PCMCIA/JEIDA Memory Cards (PC-Cards) Type I | ||
max. 1M byte SRAM 5 Volt | max. 1M byte SRAM 5 Volt | ||
| − | Display : 480* | + | Display : 480*64 pixel display (usually 80*8 characters) |
Weight : 930 g | Weight : 930 g | ||
Height : 22 mm | Height : 22 mm | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
- BBC-BASIC with Assembler support | - BBC-BASIC with Assembler support | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
=== How to get the Firmware Number? === | === How to get the Firmware Number? === | ||
| Line 86: | Line 85: | ||
=== What is inside? === | === What is inside? === | ||
| − | Inside the NC100 is a SMD layout. I have a german NC100 and the | + | Inside the NC100 is a SMD layout. I have a german NC100 and the circuit board is |
labeled Amstrad plc 4500-001P-1, NA999-32142, manual marked C (A-H) and | labeled Amstrad plc 4500-001P-1, NA999-32142, manual marked C (A-H) and | ||
1 (1-8). All IC's are SMD apart from IC303 which is on the backside of the | 1 (1-8). All IC's are SMD apart from IC303 which is on the backside of the | ||
NC100 (behind the firmware EPROM cover). On the drawing below I have | NC100 (behind the firmware EPROM cover). On the drawing below I have | ||
| − | labeled all | + | labeled all ICs, but you can find it on the layout also! |
[[File:NC100_Inside.png]] | [[File:NC100_Inside.png]] | ||
| Line 105: | Line 104: | ||
Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼───────────────────────────────────────Â | Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼───────────────────────────────────────Â | ||
║302 │NEC Japan │4*34=136│µPD 65034 ║ | ║302 │NEC Japan │4*34=136│µPD 65034 ║ | ||
| − | ║ │D65034GD093 │PLCC | + | ║ │D65034GD093 │PLCC 136│Custom ASIC ║ |
Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼───────────────────────────────────────Â | Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼───────────────────────────────────────Â | ||
║303 │NEC Japan │2*16= 32│27C2001 = CMOS EPROM 256K*8 bit ║ | ║303 │NEC Japan │2*16= 32│27C2001 = CMOS EPROM 256K*8 bit ║ | ||
| Line 144: | Line 143: | ||
╚════¤═══════════════¤════════¤═══════════════════════════════════════╝ | ╚════¤═══════════════¤════════¤═══════════════════════════════════════╝ | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
=== Amstrad NC100/NC150 Simplfied Bock Diagram === | === Amstrad NC100/NC150 Simplfied Bock Diagram === | ||
| Line 150: | Line 148: | ||
[[File:NC100_BlockDiagram.png]] | [[File:NC100_BlockDiagram.png]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | === Amstrad NC100/150 Power Supply Bock Diagram === | ||
| + | [[File:NC100_PowerSupply.png]] | ||
| − | + | == IC Pinouts == | |
| − | + | On the next pages folowing the pinouts off the most important ICs used in | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | On the next pages folowing the pinouts off the most important | + | |
the NC100. '*' indicates active Low and 'NC' is Not Connected in the NC100 | the NC100. '*' indicates active Low and 'NC' is Not Connected in the NC100 | ||
| + | === The Microprocessor (MPU, IC301) === | ||
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Type : Z84C00 | Type : Z84C00 | ||
Manufacturer : Zilog Inc. | Manufacturer : Zilog Inc. | ||
| Line 264: | Line 201: | ||
21 *MREQ 43 A9 | 21 *MREQ 43 A9 | ||
22 *IORQ 44 A10 | 22 *IORQ 44 A10 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | === The Custom Chip (IC302) === | |
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Type : µPD 65034 | Type : µPD 65034 | ||
Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | ||
| − | Description : | + | Description : Custom Chip with multiple funktions |
Process : CMOS | Process : CMOS | ||
Supply Voltage : +5V | Supply Voltage : +5V | ||
Package : PLCC 136 | Package : PLCC 136 | ||
| − | The chip has multiple | + | The chip has multiple functions: |
- Clock generator for CPU and UART | - Clock generator for CPU and UART | ||
| Line 335: | Line 256: | ||
33 X1 67 GND 101 PD0 135 GND | 33 X1 67 GND 101 PD0 135 GND | ||
34 VDD 68 GND 102 VDD 136 GND | 34 VDD 68 GND 102 VDD 136 GND | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | === The Firmware EPROM (IC303) === | |
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The Firmware EPROM (IC303) | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Type : µPD 27C2001 | Type : µPD 27C2001 | ||
Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | ||
| Line 382: | Line 293: | ||
The NC100 can also control 27C4001 (512K), 23C2001 (256K), 23C4001 (512K), | The NC100 can also control 27C4001 (512K), 23C2001 (256K), 23C4001 (512K), | ||
23C8001 (1M byte) EPROM's! By the type of the EPROM there had to be set | 23C8001 (1M byte) EPROM's! By the type of the EPROM there had to be set | ||
| − | some different connections, this connections are set by | + | some different connections, this connections are set by zero Ohm |
| − | + | SMD-resistors from the backside of the board close to IC303: | |
╔═════════Ð════════Ð══════Ð══════Ð══════Ð══════╗ | ╔═════════Ð════════Ð══════Ð══════Ð══════Ð══════╗ | ||
| Line 403: | Line 314: | ||
I have double my ROM-space by set in a 27C4001 EPROM, remove J304 and set | I have double my ROM-space by set in a 27C4001 EPROM, remove J304 and set | ||
in J301 by a pice of wire. | in J301 by a pice of wire. | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | === The Static Random Access Memory (SRAM, IC304 and IC305) === | |
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The Static Random Access Memory (SRAM, IC304 and IC305) | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Type : µPD 43257A | Type : µPD 43257A | ||
Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | ||
| Line 458: | Line 362: | ||
+ = use | + = use | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | === The PCMCIA card slot (IC306) === | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The PCMCIA card slot (IC306) | + | |
| − | + | ||
The NC-100 can use PCMCIA/JEIDA Memory Cards (PC-Cards) Type I, max. 1024K | The NC-100 can use PCMCIA/JEIDA Memory Cards (PC-Cards) Type I, max. 1024K | ||
| Line 486: | Line 373: | ||
place. Data transfers are then be done in sector chunks. | place. Data transfers are then be done in sector chunks. | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
PCMCIA Card Connector Type I, 5 Volts: | PCMCIA Card Connector Type I, 5 Volts: | ||
| Line 536: | Line 424: | ||
34 GND 68 GND | 34 GND 68 GND | ||
RFU = Reserved Future Use | RFU = Reserved Future Use | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | === The Real-Time-Clock (RTC, IC307) === | |
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The Real-Time-Clock (RTC, IC307) | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Type : TC8521AP/AM | Type : TC8521AP/AM | ||
Manufacturer : Toshiba Corporation | Manufacturer : Toshiba Corporation | ||
| Line 561: | Line 445: | ||
- Built-in 26*4 bit RAM | - Built-in 26*4 bit RAM | ||
- 4-bit bidirectional data bus | - 4-bit bidirectional data bus | ||
| − | - 4-bit | + | - 4-bit address input |
- Directly connectable with CPU bus | - Directly connectable with CPU bus | ||
- Capable of battery backup | - Capable of battery backup | ||
| Line 588: | Line 472: | ||
19 XOUT | 19 XOUT | ||
20 VCC | 20 VCC | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | === The Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART, IC308) === | |
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART, IC308) | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Type : µPD 71051 | Type : µPD 71051 | ||
Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | ||
| Line 655: | Line 522: | ||
27 D0 | 27 D0 | ||
28 D1 | 28 D1 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | === The RS232-Driver (IC309) === | |
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The RS232-Driver (IC309) | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Type : µPD 4711A | Type : µPD 4711A | ||
Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | Manufacturer : NEC Electronics | ||
| Line 737: | Line 589: | ||
homepage: http://www.germany.net/teilnehmer/101.107378/index.htm | homepage: http://www.germany.net/teilnehmer/101.107378/index.htm | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:NC Series]][[Category:Amstrad Products]][[Category:Non CPC Computers]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:11, 11 July 2023
Contents
- 1 A Surgical Guide To The Amstrad Notepad Computer
- 2 IC Pinouts
- 2.1 The Microprocessor (MPU, IC301)
- 2.2 The Custom Chip (IC302)
- 2.3 The Firmware EPROM (IC303)
- 2.4 The Static Random Access Memory (SRAM, IC304 and IC305)
- 2.5 The PCMCIA card slot (IC306)
- 2.6 The Real-Time-Clock (RTC, IC307)
- 2.7 The Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART, IC308)
- 2.8 The RS232-Driver (IC309)
- 2.9 The RS232-connector pinout
A Surgical Guide To The Amstrad Notepad Computer
This page is based on Hans-Jürgen Böhling's "surgical guide to the Amstrad NC". The original document is avaliabe here [1] (author's website) or here Media:sg-nc100.zip (local copy)
Amstrad Notepad Computer - What is it?
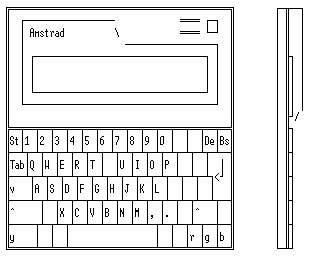
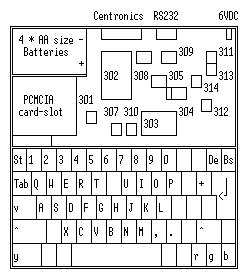
The model NC100 is about DIN A4 size with a LCD 8 lines * 80 characters screen, nearly full size keyboard, a PCMCIA memory card slot on the right hand side and four coloured keys. The Notepads have standard Centronics parallel port (DB-25 pin famale connector) and RS232 (DB 9 pin male) serial port. The system has drivers for 9 and 24 pin dot matrix, Canon inkjet and Laserjet printers. The serial connector support 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, or 9600 bps. As power supply the NC100 use 4 * AA sice batteries or an AC adapter. As backup battery ther is also a CR2032 3 Volt lithium cell.
The model NC150 (it seems) is retailing only in Italy and Fance. It has 512K bytes firmware ROM and 128K RAM. The extra 256K bytes ROM contains a spreadsheet and the arcade game 'BLOCKADE' (similar to TETRIS).
The model NC200 include the additional features of the NC150 but also a 720K MS-DOS compatible 3.5 inch floppy disk drive and a 16 lines by 80 characters screen witch had to be fold up like a laptop.
Specifications
Model : NC100
Processor : Z80 compatible CMOS
Operating
frequency : 4.606 MHz
Memory : 64K byte internal
(15K system-, 11K upper-, 38K lower memory)
Storage : PCMCIA/JEIDA Memory Cards (PC-Cards) Type I
max. 1M byte SRAM 5 Volt
Display : 480*64 pixel display (usually 80*8 characters)
Weight : 930 g
Height : 22 mm
Width : 295 mm
Length : 210 mm
Power Consumption ON : 40 - 60 mA
Built in firmware : 256K byte with
- Texteditor with mailmerge and spellchecker
- Address book
- Time manager (diary with alarm-clock)
- Calculator
- Terminal-programm (serial Tranfer with ASCII or XModem)
- BBC-BASIC with Assembler support
How to get the Firmware Number?
When you are in the main Menu (text editor, calculater, calender) push the secret-button and the system-settings menu appears, the version number will be shown in the first line of the sceen. I have a german NC100 and the firmware number is v1.06.
PCMCIA Memory Cards
A battery buffered PCMCIA SRAM-Memory Card will preserve you from data loss even if your Notepad crashes and increases the available memory. It also allows you to create a file with BBC-BASIC bigger than 1024 bytes. This is because BBC-BASIC allocates all available memory on startup except 1024 bytes. The maximum size to use with the NC100 is up to 1M byte.
How to open the NC100?
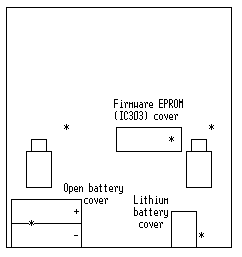
Before disassembling the Notepad you should save all your data! Then put the Notepad on the table face down. Remove the four AA size batteries, then unscrew the five screws (one under the battery cover). In the drawing below they are marked with a "*"-sign. One screw fixes the cover of the firmware EPROM.Place the Notepad the right way up and lift off the upper part of the case. Be careful, because the display is still connected to the main-board via a folio-flat-cable and so is the speaker! Don't be nervous, the cables can be simply pulled out of their sockets. Now you can separate the covers.
What is inside?
Inside the NC100 is a SMD layout. I have a german NC100 and the circuit board is labeled Amstrad plc 4500-001P-1, NA999-32142, manual marked C (A-H) and 1 (1-8). All IC's are SMD apart from IC303 which is on the backside of the NC100 (behind the firmware EPROM cover). On the drawing below I have labeled all ICs, but you can find it on the layout also!
The table below gives a description of the IC's in the NC100:
╔════Ð═══════════════Ð════════Ð═══════════════════════════════════════╗ ║IC-#│Label │Pin's │Description ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║301 │ZILOG │4*11= 44│Z84C00 ║ ║ │Z84C0006FEC │PLCC 44 │CMOS, 6 MHz ║ ║ │Z80 CPU │ │Z80 compatible Microprocessor ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║302 │NEC Japan │4*34=136│µPD 65034 ║ ║ │D65034GD093 │PLCC 136│Custom ASIC ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║303 │NEC Japan │2*16= 32│27C2001 = CMOS EPROM 256K*8 bit ║ ║ │D27C2001 │DIL 32 │Firmware EPROM ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║304 │NEC JAPAN │2*14= 28│µPD 43257 A = CMOS SRAM 32K*8 bit ║ ║ │D43257AGU-10LL │SO 28 │Memory layouted as an SO 32 (32 pin)! ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║305 │NEC Japan │2*14= 28│µPD 43257 A = CMOS SRAM 32K*8 bit ║ ║ │D43257AGU-10LL │SO 28 │Memory ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║306 │MEMORY CARD │2*34= 68│PCMCIA/JEIDA Memory Cards Slot Type I ║ ║ │ │PCMCIA │for max. 1M byte SRAM Memory, 5 Volt ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║307 │T 9224 HB │2*10= 20│TC8521 ║ ║ │ 8521 AM │SO 20 │Real-Time-Clock ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║308 │NEC Japan │2*14= 28│µPD 71051 ║ ║ │D71051 GU │SO 28 │UART (parallel to seriell transpose) ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║309 │NEC Japan │2*10= 20│µPD 4711 ║ ║ │D4711 AG │SO 20 │RS232-driver (shift level to +/- 10V) ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║310 │not placed │2* 7= 14│74HC00 = CMOS-Logic 4 * NAND ║ ║ │ │SO 14 │(only used if IC304/IC305 = 43256) ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║311 │D4584G │2* 7= 14│4584 = CMOS-Logic 6 * Schmitt-Trigger ║ ║ │ │SO 14 │ ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║312 │C339 G │2* 7= 14│LM339 = 4 * Comparator ║ ║ │ │SO 14 │(used for battery level detection) ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║313 │D4013G │2* 7= 14│4013 = CMOS-Logic 2 * D-Flip Flop ║ ║ │ │SO 14 │with set and reset ║ Ã────┼───────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────────────────── ║314 │D4584G │2* 7= 14│4584 = CMOS-Logic 6 * Schmitt-Trigger ║ ║ │ │SO 14 │ ║ ╚════¤═══════════════¤════════¤═══════════════════════════════════════╝
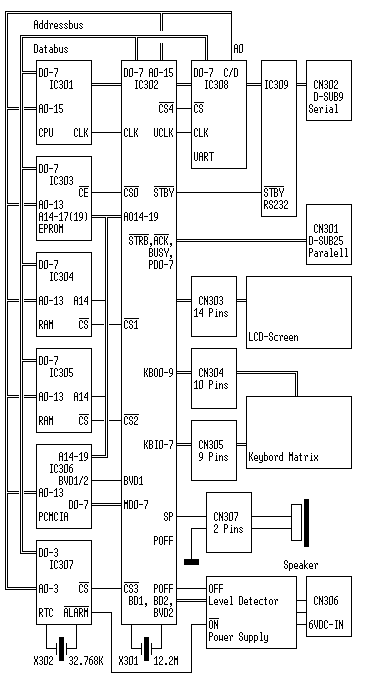
Amstrad NC100/NC150 Simplfied Bock Diagram
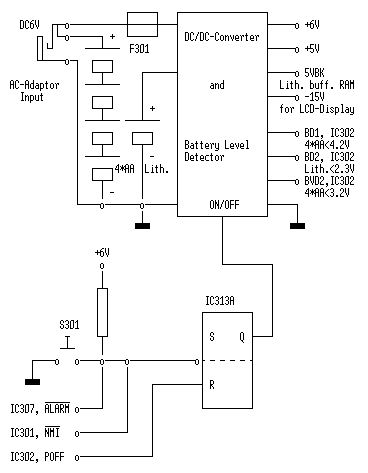
Amstrad NC100/150 Power Supply Bock Diagram
IC Pinouts
On the next pages folowing the pinouts off the most important ICs used in the NC100. '*' indicates active Low and 'NC' is Not Connected in the NC100
The Microprocessor (MPU, IC301)
Type : Z84C00 Manufacturer : Zilog Inc. Description : Microprocessor, 8-Bit Power Consumption : 15 mA typ. at 6 MHz Process : CMOS Supply Voltage : +5V Operating frequency max. : 6 MHz Package : PLCC 44 pin Features : - Commands compatible with Zilog Z80 MPU - Powerful set of 158 instructions including the 78 of the 8080A - 10 addressing modes - Power down mode when the system clock is stopped Pinout : 1 A11 23 *RD 2 A12 24 NC 3 A13 25 NC 4 A14 26 *WR 5 A15 27 *BUSACK 6 NC 28 *WAIT 7 CLK 29 *BUSREQ 8 D4 30 *RESET 9 D3 31 *M1 10 D5 32 *RFSH 11 D6 33 GND 12 NC 34 A0 13 VCC 35 A1 14 D2 36 A2 15 D7 37 A3 16 D0 38 A4 17 D1 39 A5 18 *INT 40 A6 19 *NMI 41 A7 20 *HALT 42 A8 21 *MREQ 43 A9 22 *IORQ 44 A10
The Custom Chip (IC302)
Type : µPD 65034 Manufacturer : NEC Electronics Description : Custom Chip with multiple funktions Process : CMOS Supply Voltage : +5V Package : PLCC 136 The chip has multiple functions: - Clock generator for CPU and UART - Peripher Interface Adaptor (to printer, LCD-screen, keybord,) - Memory Management Unit - PCMCIA-Interface - Sound generator for speaker Pinout : 1 VDD 35 GND 69 VDD 103 GND 2 KBI1 36 GND 70 TEMP 104 GND 3 KBI5 37 AO18 71 UCLK 105 *STRB 4 KBI7 38 AO19 72 RRDY 106 *CD2 5 KBI6 39 GND 73 TRDY 107 *CD1 6 KBI4 40 CLK 74 *STBY 108 *CE1 7 KBI3 41 HALT 75 LD0 109 *OE1 8 KBI2 42 *MREQ 76 LD1 110 *WE1 9 KBI0 43 *IORQ 77 LD2 111 *REG 10 A0 44 *BACK 78 LD3 112 BVD2 11 A1 45 *BREQ 79 FRM 113 BVD1 12 A2 46 *WAT 80 DF 114 WP 13 A3 47 *M1 81 LOAD 115 MD3 14 A4 48 *INT 82 CP 116 MD4 15 A5 49 *RD 83 POFF 117 MD5 16 A6 50 *WR 84 SP 118 GND 17 GND 51 DO 85 GND 119 MD6 18 GND 52 D1 86 GND 120 MD7 19 A7 53 D2 87 BD1 121 MD0 20 A8 54 D3 88 BD2 122 MD1 21 A9 55 GND 89 *NMIC 123 MD2 22 A10 56 D4 90 *RES 124 TEST (NC) 23 A11 57 D5 91 URES 125 KBO9 24 A12 58 D6 92 *BUSY 126 KBO8 25 A13 59 D7 93 *ACK 127 KBO7 26 A14 60 RRD 94 PD7 128 KBO6 27 A15 61 *CS0 95 PD6 129 KBO1 28 AO14 62 *CS1 96 PD5 130 KBO2 29 AO15 63 *CS2 97 PD4 131 KBO5 30 AO16 64 *CS3 98 PD3 132 KBO4 31 AO17 65 *CS4 99 PD2 133 KBO3 32 X2 66 TRXC 100 PD1 134 KBO0 33 X1 67 GND 101 PD0 135 GND 34 VDD 68 GND 102 VDD 136 GND
The Firmware EPROM (IC303)
Type : µPD 27C2001
Manufacturer : NEC Electronics
Description : EPROM, 2Mb, 8-Bit, UV-eraseable
Org. : 256K x 8 Bit
Process : CMOS
Supply Voltage : +5V
Standby : 0.5 mW
Operation : 150 mW
Package : DIL
Pinout :
1 NC (A19) 17 O3
2 A16 18 O4
3 A15 19 O5
4 A12 20 O6
5 A7 21 O7
6 A6 22 *CE
7 A5 23 A10
8 A4 24 *OE
9 A3 25 A11
10 A2 26 A9
11 A1 27 A8
12 A0 28 A13
13 O0 29 A14
14 O1 30 A17
15 O2 31 NC (A18)
16 GND 32 VCC
The NC100 can also control 27C4001 (512K), 23C2001 (256K), 23C4001 (512K),
23C8001 (1M byte) EPROM's! By the type of the EPROM there had to be set
some different connections, this connections are set by zero Ohm
SMD-resistors from the backside of the board close to IC303:
╔═════════Ð════════Ð══════Ð══════Ð══════Ð══════╗
║ IC303 │ Kbyte │ J301 │ J302 │ J303 │ J304 ║
╠═════════Ï════════Ï══════Ï══════Ï══════Ï══════╣
║ 27C2001 │ 256 │ │ │ + │ + ║
Ã─────────┼────────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────Â
║ 27C4001 │ 512 │ + │ │ + │ ║
╠═════════Ï════════Ï══════Ï══════Ï══════Ï══════╣
║ 23C2001 │ 256 │ │ │ + │ + ║
Ã─────────┼────────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────Â
║ 23C4001 │ 512 │ │ + │ │ + ║
Ã─────────┼────────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────Â
║ 23C8001 │ 1024 │ + │ + │ │ ║
╚═════════¤════════¤══════¤══════¤══════¤══════╝
+ = use
I have double my ROM-space by set in a 27C4001 EPROM, remove J304 and set
in J301 by a pice of wire.
The Static Random Access Memory (SRAM, IC304 and IC305)
Type : µPD 43257A
Manufacturer : NEC Electronics
Description : SRAM, 256K Bit
Org. : 32K x 8 Bit
Process : CMOS
Supply Voltage : +5VBK (Lithium battery buffered)
Standby : 0.5 mW
Operation : 225 mW
Package : SO 28
Pinout :
1 A14 15 DQ4
2 A12 16 DQ5
3 A7 17 DQ6
4 A6 18 DQ7
5 A5 19 DQ8
6 A4 20 *CS
7 A3 21 A10
8 A2 22 *OE
9 A1 23 A11
10 A0 24 A9
11 DQ1 25 A8
12 DQ2 26 A13
13 DQ3 27 *WE
14 GND 28 VCC
On my NC100 the IC304 is layouted as an SO 32 (32 pin). I belief you can
put some bigger RAM-chip in the circuit, but there is nothing about that in
the electronic diagram! There is only that the NC100 can control a 43256
RAM-chips. By the type of the RAM-chip there had to be set some different
connections and use IC310:
╔═══════════Ð══════Ð══════Ð══════Ð══════Ð═══════╗
║IC304, 305 │ J305 │ J306 │ J307 │ J308 │ IC310 ║
╠═══════════Ï══════Ï══════Ï══════Ï══════Ï═══════╣
║43256 │ + │ │ │ │ + ║
Ã───────────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼───────Â
║43257 │ │ + │ + │ + │ ║
╚═══════════¤══════¤══════¤══════¤══════¤═══════╝
+ = use
The PCMCIA card slot (IC306)
The NC-100 can use PCMCIA/JEIDA Memory Cards (PC-Cards) Type I, max. 1024K (1M) byte static ram card, 5 Volts. You can bye them in 64Kb, 128Kb, 256Kb, 512Kb, and 1024Kb sizes. The flash memory cards are not suitable for the NC-100. These have a control register that must be written to before any read or write can take place. Data transfers are then be done in sector chunks.
PCMCIA Card Connector Type I, 5 Volts:
1 mm 1 mm
││ ││
││ 34 1 ││
┌───────────────────────────────────────────┐│────────────
1.6 mm ───└┐ ■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■ ││ 3.4 mm
───┌┘ ■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■ └┐─── 1 mm
└────────────────────────────────────────────┘────────────
│ 68 35 │
│ 54 mm │
PCMCIA Version 2.0 Pinout:
1 GND 35 GND
2 D3 I/O 36 *CD1 O
3 D4 I/O 37 D11 I/O (NC)
4 D5 I/O 38 D12 I/O (NC)
5 D6 I/O 39 D13 I/O (NC)
6 D7 I/O 40 D14 I/O (NC)
7 *CE1 I 41 D15 I/O (NC)
8 A10 I 42 *CE2 I (NC)
9 *OE I 43 RFSH I (NC)
10 A11 I 44 RFU I (NC)
11 A9 I 45 RFU I (NC)
12 A8 I 46 A17 I
13 A13 I 47 A18 I
14 A14 I 48 A19 I
15 *WE/PGM I 49 A20 I (NC)
16 RDY/*BSY O 50 A21 I (NC)
17 VCC 51 VCC
18 VPP1 52 VPP2
19 A16 I 53 A22 I (NC)
20 A15 I 54 A23 I (NC)
21 A12 I 55 A24 I (NC)
22 A7 I 56 A25 I (NC)
23 A6 I 57 RFU (NC)
24 A5 I 58 RESET I (NC)
25 A4 I 59 *WAIT O (NC)
26 A3 I 60 RFU (NC)
27 A2 I 61 *REG I
28 A1 I 62 BVD2 O
29 A0 I 63 BVD1 O
30 D0 I/O 64 D8 I/O (NC)
31 D1 I/O 65 D9 I/O (NC)
32 D2 I/O 66 D10 I/O (NC)
33 WP O 67 *CD2 O
34 GND 68 GND
RFU = Reserved Future Use
The Real-Time-Clock (RTC, IC307)
Type : TC8521AP/AM Manufacturer : Toshiba Corporation Description : Real Time Clock Process : CMOS Supply Voltage : +5VBK (Lithium battery buffered) Power Dissipat. max : 1.25 mW Package : SO 20 Features : - Clock funktion (hr, min, sec, date, day of week, year and leap year) auto-calendar - Clock system of 24-hour or 12-hour selectable - +/- 30 sec correction funktion - Alarm signal or pulse of 16Hz or 1Hz can be output - Built-in 26*4 bit RAM - 4-bit bidirectional data bus - 4-bit address input - Directly connectable with CPU bus - Capable of battery backup Pinout : 1 *CS 2 CS 3 ADJ 4 A0 5 A1 6 A2 7 NC 8 A3 9 *RD 10 GND 11 *WR 12 D0 13 D1 14 D2 15 D3 16 *ALARM 17 NC 18 XIN 19 XOUT 20 VCC
The Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART, IC308)
Type : µPD 71051 Manufacturer : NEC Electronics Description : UART Serial Control Unit Process : CMOS Supply Voltage : +5V Package : SO 28 Features : - Synchronous and asynchronous operation - Full duplex, double buffered transmitter / receiver - Error detektion at parity, overrun and framing - 5 to 8 bit characters - Low power standby mode - Functionally equivalant to the 8251A UART Pinout : 1 D2 2 D3 3 RxDA TA 4 GND 5 D4 6 D5 7 D6 8 D7 9 *TxCLK 10 *WR 11 *CS 12 C/*D 13 *RD 14 RxRDY 15 TxRDY 16 SYNCBRK (NC) 17 *CTS 18 TxE MP 19 TxDA TA 20 CLK 21 RES ET 22 *DSR (NC) 23 *RTS 24 *DTR (NC) 25 *RxCLK 26 Vdd 27 D0 28 D1
The RS232-Driver (IC309)
Type : µPD 4711A Manufacturer : NEC Electronics Description : RS232-Driver Process : MOS-IC Supply Voltage : +5V Power Dissipat. : 60 mA Package : SO 20 The RS232-driver shift up the TTL-level (0V/+5V) output from UART to RS232-level (+10V/-10V). Pinout : 1 Vdd 2 C1+ 3 Vcc 4 C1- 5 STB 6 Din1 7 Din2 8 Rout 1 9 Rout 2 10 GND 11 Rcon 12 Rin2 13 Rin1 14 Dout 2 15 Dout1 16 Dcon 17 Vss 18 C4- 19 GND 20 C4+
The RS232-connector pinout
(DTR just duplicates RTS)
Pin I/O Description 5 GND Signal Ground 9 <─ RI Ring Indicator (NC) 4 ─> DTR Data Terminal Ready 8 <─ CTS Clear To Send 3 ─> TD Transmit Data 7 ─> RTS Request To Send 2 <─ RD Receive Data 6 <─ DSR Data Set Ready (NC) 1 <─ CD Carrier Detect (NC)
Author:
Hans-Jürgen Böhling Bülowstr. 2 40476 Düsseldorf Germany e-mail : 101.107378@germanynet.de homepage: http://www.germany.net/teilnehmer/101.107378/index.htm