Intro
This interface was originally described in the book "Maschinenspracheprogramme und Hardware-Erweiterungen für Schneider CPC's" written by Paul Bauriedl, released by IDEA Verlag in 1987. Around mid-nineties, Tim Riemann has circulated the schematic as GIG in the internet.
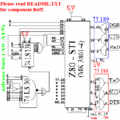
The circuit is very similar (or possibly indentical) to the Schneider RS232 Interface, both circuits are using a Z80 STI, both mapped to the same I/O port addresses. Whether or not the circuits are fully compatible with each other is unknown. Some small details might differ. For example, the clock source being passed to the Z80 STI chip could be different.
How to build a RS232 - Interface for the CPC-Series!
Schematic and source code
First about the connection plan: You need a power supply that supports +9V,-9V and 5V. Connect all pins. You have to connect D0..D7 from the adressbus with the Z80 STI. You have to connect D0 with pin 21, D1 with pin 22, ..., D7 with pin 28. That's all. Now you can plug in the interface in the CPC. Switch the power on. If the CPC doesn't work normal please switch the power off and you have to watch for faults in the connection of your interface :-(. If everything is ok then you have to copy the assembler code and do the next test.
Second part: How to program the interface. (The assembler code is saved in RS232.ASM)
Z80-STI: 50 to 19200 bps (5,6,7 or 8 bit, 1, 1 1/2, 2 stopbits, all parity flags) 24 registers, use 16 registers (direct) with F8E0-F8EF, the last 8 registers can be used indirect with a special register
The meaning and the Addresses of the registers
Register 0 (Port F8E0h)
This register transfers data from and to a indirect register.
Register 1 (Port F8E1h)
This register transfers the data from and to the I/O port of the chip. If you use V24 you can request handshake signals from this port. In this interface the following bits have this meaning:
Bit 0: DTR (Data Terminal Ready) Bit 1: RTS (Ready to Send) Bit 2: CTS (Clear to Send) Bit 3: DSR (Data Set Ready) Bit 4-7: not used
Register 2-7 (Port F8E2h-F8E7h)
These registers are used by the interrupt handler. If you want to know what you can do with this registers please write to Mostek for support.
Register 8 (Port F8E8h)
Bit 3-7 are used by the interrupt handler. With bit 0-2 you can choose the indirect register.
Register 9 (Port F8E9h)
Control register for timer A and B. You needn't to use the timer for a V24 interface.
Register 10 (Port F8EAh)
Timer B value
Register 11 (Port F8EBh)
Timer A value
Register 12 (Port F8ECh)
USART-register. Change the connect-parameters.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
x x x x x x x 0
^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^
| | | | | | 1=even
| | | | | | 0=odd
| | | | | 1=Parity on
| | | | | 0=Parity off
| | | Startbit Stopbit Format
| | | 0 0 = 0 0 synchron
| | | 0 1 = 1 1 asynchron
| | | 1 0 = 1 1 1/2 asynchron
| | | 1 1 = 1 2 asynchron
| 0 0 = 8 Bit
| 0 1 = 7 Bit
| 1 0 = 6 Bit
| 1 1 = 5 Bit
please always set on 0
Register 13 (Port F8EDh)
Receiver status. You need only the following bits:
Bit 0: Receiver-Enable, set to 1 if receiving is possible.
Bit 1: Memory full "1" or not "0". (If 8 Bits are
received then the interface send memory full).
Register 14 (Port F8EEh)
Sending status. Again you need only two bits:
Bit 0: Sending-Enable, must set to "1" if sending is allowed.
Bit 7: Memory full "1" or not "0". This bit can
be used to ask if a word is send or not.
Register 15 (Port F8EFh)
This is the send and receive register. Here you can get a word or send a word.
Indirect registers (Choose them with register 8)
register 0: Not used.
register 1: Data for Timer D.
register 2: Data for Timer C.
register 3: Not used.
register 4: Not used.
register 5: Not used.
register 6: I/O-Port (receive or send). High means sending, low receiving.
register 7: Used for Timer C and D. Reset with "1".
For more exact informations please write to Mostek and ask for support for the Z80-STI. You also can look at the assembler code.
About the assembler code
The program RS232.ASM installs 2 new BASIC commands (|FORMAT, |RECORD, |SEND). Here you can read the description about this new commands:
|FORMAT, number of bps, number of stop-bits, data bits, parity on/off, parity even/odd
Number of bps:
0 = 50 bps
1 = 75 bps
2 = 110 bps
3 = 150 bps
4 = 300 bps
5 = 600 bps
6 = 1200 bps
7 = 2400 bps
Number of stop bits: 1 = 1 stop bit 0 = 2 stop bit
Data bits: 0 = 7 data bits 1 = 8 data bits
Parity: 1 = even 0 = odd
Parity: 1 = on 0 = off
Normally, you use 8N1 for connection with BBS's you can initialise this with |FORMAT, number of bps, 1, 1, 0, 1.
|RECORD, @a$
The incoming chars will be read in a string. Control codes will be send to the
string, too, because sometimes you need it for binary transmissions.
|SEND, @a$
The string is send until it ends, except you press ESC. The program will not
send CR or LF, so you can use this for binary transmission.
Used components:
- 1x Z80-STI (MK3801-4)
- 1x SN75189
- 1x SN75188
- 1x 74LS30
- 1x 74LS138
- 1x 74LS20
- 1x 74LS04
- 1x 74LS32
- 1x 25pin SUB-D connector (male)
- 1x connector for the expansion port
Note: The 74LS20, 74LS04, 74LS32 are the smaller logic symbols in the schematic.
Downloads
File:Rs232cpc.lzh - All info and files on topic