Difference between revisions of "Programming:Unlocking ASIC"
(→In Z80 Assembler) |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
ld hl,sequence | ld hl,sequence | ||
ld e,17 | ld e,17 | ||
| + | |||
.seq | .seq | ||
ld a,(hl) | ld a,(hl) | ||
| Line 46: | Line 47: | ||
dec e | dec e | ||
jr nz,seq | jr nz,seq | ||
| + | |||
ei | ei | ||
ret | ret | ||
| Line 63: | Line 65: | ||
== In Z80 Assembler == | == In Z80 Assembler == | ||
| − | This allowed [[Madram]] to create this optimized unlock routine: | + | This allowed [[Madram]] to create this optimized lock-unlock routine: |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
UnlockAsic | UnlockAsic | ||
| Line 71: | Line 73: | ||
out (c),0 | out (c),0 | ||
ld hl,%1001000011101010 | ld hl,%1001000011101010 | ||
| + | |||
.loop | .loop | ||
out (c),c | out (c),c | ||
| Line 79: | Line 82: | ||
cp #4D | cp #4D | ||
jr nz,.loop | jr nz,.loop | ||
| + | |||
ld a,#CD ; a=#CD for unlock, another value for lock | ld a,#CD ; a=#CD for unlock, another value for lock | ||
| − | out (c),a : out (c),a | + | out (c),a:out (c),a |
| + | ei | ||
| + | ret | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another optimized unlock routine by [[Urusergi]]: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | di | ||
| + | ld bc,#BCFF | ||
| + | out (c),c | ||
| + | out (c),0 | ||
| + | ld a,c | ||
| + | |||
| + | .loop | ||
| + | out (c),a | ||
| + | ld d,a ; D = 7654 3210 | ||
| + | rlca:rlca ; A = 5432 1076 | ||
| + | xor d:and #7F:xor d ; A = 7432 1076 | ||
| + | ld e,a | ||
| + | rlca ; A = 4321 0767 | ||
| + | xor e ; A = 7432 1076 XOR 4321 0767 | ||
| + | rrc d ; D = 0765 4321 | ||
| + | xor d:and #88:xor d ; A = (7 xor 4)765 (1 xor 0)321 | ||
| + | cp c | ||
| + | jr nz,.loop | ||
| + | |||
ei | ei | ||
ret | ret | ||
Revision as of 11:22, 18 March 2025
To unlock the ASIC, a 17-byte "unlock" sequence must be sent to the CRTC's selection port (&BC00) : RQ00, 0, 255, 119, 179, 81, 168, 212, 98, 57, 156, 70, 43, 21, 138, STATE, <ACQ>
- RQ00 must be different from the value 0.
- STATE=205 for UNLOCK otherwise another value for LOCK.
- ACQ represents sending any value if STATE=205 (not needed otherwise).
Note: the ASIC is already unlocked after the STATE phase, before ACQ. So ACQ is actually never needed.
Once the ASIC is unlocked, we get access to a new Gate Array register called RMR2. It is accessible in the same way as other Gate Array registers.
Contents
BASIC version
10 RESTORE 20 FOR x=0 TO 16:READ a:OUT &BC00,a:NEXT 30 DATA 255,0,255,119,179,81,168,212,98,57,156,70,43,21,138,205,238 40 PRINT"ASIC unlocked!"
Z80 Assembler version
;; This example shows how to unlock the ASIC ;; ;; This example is designed for CPC+ only and will ;; not work on CPC or KC Compact. ;; ;; This example will compile with the MAXAM assembler ;; or the built-in assembler of WinAPE32. org &8000 ;;-------------------------------------------------- ;; Unlock CPC+ additional features di ld b,&bc ld hl,sequence ld e,17 .seq ld a,(hl) out (c),a inc hl dec e jr nz,seq ei ret ;;---------------------------------------------------------- ;; this is the sequence to unlock the ASIC extra features .sequence defb &ff,&00,&ff,&77,&b3,&51,&a8,&d4,&62,&39,&9c,&46,&2b,&15,&8a,&cd,&ee
Optimized version
The unlocking sequence can be reconstituted from simple bit operations instead of being stored in memory.
In Z80 Assembler
This allowed Madram to create this optimized lock-unlock routine:
UnlockAsic di ld bc,#BCFF out (c),c out (c),0 ld hl,%1001000011101010 .loop out (c),c ld a,h:rlca:ld h,l:ld l,a srl c xor c:and #88:xor c ld c,a cp #4D jr nz,.loop ld a,#CD ; a=#CD for unlock, another value for lock out (c),a:out (c),a ei ret
Another optimized unlock routine by Urusergi:
di ld bc,#BCFF out (c),c out (c),0 ld a,c .loop out (c),a ld d,a ; D = 7654 3210 rlca:rlca ; A = 5432 1076 xor d:and #7F:xor d ; A = 7432 1076 ld e,a rlca ; A = 4321 0767 xor e ; A = 7432 1076 XOR 4321 0767 rrc d ; D = 0765 4321 xor d:and #88:xor d ; A = (7 xor 4)765 (1 xor 0)321 cp c jr nz,.loop ei ret
In Python
def unlock_asic():
b, c, h, l = 0xBC, 0xFF, 0x90, 0xEA # Initialize registers
port_out(b, c)
port_out(b, 0)
while c != 0x4D:
port_out(b, c)
h, l = l, ((h << 1) | (h >> 7)) & 0xFF # Rotate h and swap h, l
c = ((c >> 1) & ~(1 << 3)) | (l & 0x88) # Modify c
port_out(b, 0xCD)
port_out(b, 0xCD)
def port_out(port, value):
print(f"Port: {hex(port)}xx Out: {hex(value)}")
unlock_asic()
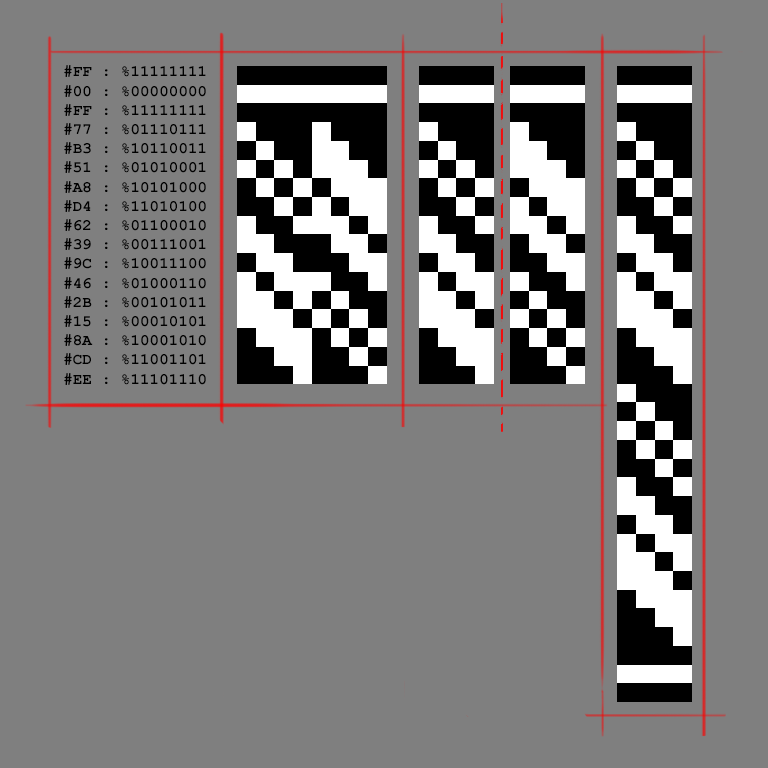
Visual representation
As one may see, the nybbles in the sequence are based on two 4bit shift registers.
Visual by Hwikaa
Patent
For one reason or another, Amstrad has patented the verification mechanism (GB2243701A).
The patent seems to focus on verifying (rather than on sending) the sequence, so its legal use is a bit unclear.
On the Original Arnold V Specs - Issue 1.5 - 10th April 1990, it is precised at §2.11 "Locking of enhanced features":
it should be noted that unauthorised use of this mechanism may infringe Amstrad's patent.