Difference between revisions of "ROM"
(Created page with "== What Exactly are Internal and Expansion ROMs == The CPC hardware is designed to (theoretically) take up to 256 external ROMs, each ROM can be up to 16K and are numbered start...") |
(→Reserved ROM Numbers) |
||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
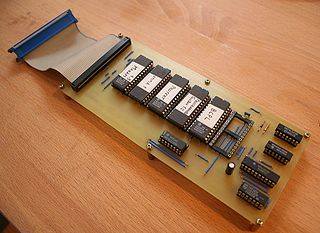
| + | [[Image:Rom_Expander.jpg|right|thumb|320px|A conventional ROMBoard for six expansion ROMs]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== What Exactly are Internal and Expansion ROMs == | == What Exactly are Internal and Expansion ROMs == | ||
| − | The CPC hardware is designed to (theoretically) take up to 256 external ROMs, each ROM can be up to 16K and are numbered starting from 0. Each ROM can contain one or more programs or utilities. These ROMs are known as Upper ROMs. The programs are started using an "RSX" command: ie: A command with the bar "|" in front - eg: the command |M is used to to start [[Maxam|Maxam]]. Standard ROMBoards such as the [[Rombo_Rombox|Rombo ROMBox]] or modern solutions such as Inicrons [[Inicron_ROM-RAM-Box|ROM-RAM-Box]] or the [[MegaFlash|MegaFlash]] allow you to attach and use these ROM programs on a CPC. Older ROMBoards usually only supported 6 or 8 ROMs and each ROM was an individual EPROM chip. Whereas modern versions ([[SF2|SF2]], [[Inicron_ROM-RAM-Box|ROM-RAM-Box]], [[Ramcard_128|Ram7s RamCard]], [[MegaROM|MegaROM]], [[MegaFlash|MegaFlash]]) support up to 32 ROMs and have combined several virtual ROMs within a single larger chip. | + | The CPC hardware is designed to (theoretically) take up to 256 external ROMs, each ROM can be up to 16K and are numbered starting from 0. Each ROM can contain one or more programs or utilities. These ROMs are known as Upper ROMs and sometimes referred to as sideways ROMs. The programs are started using an "RSX" command: ie: A command with the bar "|" in front - eg: the command |M is used to to start [[Maxam|Maxam]]. Standard ROMBoards such as the [[Rombo_Rombox|Rombo ROMBox]] or modern solutions such as Inicrons [[Inicron_ROM-RAM-Box|ROM-RAM-Box]] or the [[MegaFlash|MegaFlash]] allow you to attach and use these ROM programs on a CPC. Older ROMBoards usually only supported 6 or 8 ROMs and each ROM was an individual EPROM chip. Whereas modern versions ([[SF2|SF2]], [[Inicron_ROM-RAM-Box|ROM-RAM-Box]], [[Ramcard_128|Ram7s RamCard]], [[MegaROM|MegaROM]], [[MegaFlash|MegaFlash]]) support up to 32 ROMs and have combined several virtual ROMs within a single larger chip. |
Many programs and utilities were released on ROM for three good reasons: | Many programs and utilities were released on ROM for three good reasons: | ||
| Line 8: | Line 11: | ||
* They are always present in the background and can be called/started without needing to insert a disk or tape - Useful for utilities such as Basic extensions or Disc utilities. | * They are always present in the background and can be called/started without needing to insert a disk or tape - Useful for utilities such as Basic extensions or Disc utilities. | ||
* They usually run directly from the ROM, not from RAM, so the RAM is still 99.9% empty - Useful for text editors and compilers because the RAM is free to be used for data. | * They usually run directly from the ROM, not from RAM, so the RAM is still 99.9% empty - Useful for text editors and compilers because the RAM is free to be used for data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | No games were ever released on ROM, probably due to the 16K size limit and the fact that very few CPC users owned a ROMBoard. | ||
== The Hardware == | == The Hardware == | ||
| − | + | [[Image:MegaFlash_Final.jpg|thumb|280px|right|The MegaFlash - A 32 Position combined ROMBoard]] | |
| − | + | The CPC can choose which ROM chip is associated with the 16K area starting at &C000. This is usually the reserved for the contents of the screen (RAM), but the address range is shared with ROM Memory. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | On start up, the CPC checks whether any ROMs are installed using the "KL_ROM_WALK" firmware routine. The CPC464 only checks for ROMs in positions 7-0, but the 6128 checks for ROMs in positions 15-0. The ROMs are scanned in the reverse order starting from 7 or 15 depending on the CPC type. If a ROM is present, the CPC reads what commands the ROM offers and saves them in a table in RAM. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Further detailed information on the ROM bank numbering can be found [[Upper_ROM_Bank_Number|here]] | |
| − | + | A full list of all ROMBoards available for the CPC can be found [[Peripherals#ROM_Box_.2F_ROM_Board|here]] | |
| − | + | The plans for many DIY ROMBoards can also be found [[DIY#ROM_.2F_RAM_Expansions|here]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Reserved ROM Numbers == | |
| + | There are two special ROM positions: ROM 0 is reserved for Basic (known as a type &80 ROM - Foreground ROM) and ROM 7 is reserved for the Disc Operating System - Not present on a 464, AMSDOS on a 6128. | ||
| + | The CPC464 has one internal upper ROM (ROM 0) which can be overwritten by a ROMBoard to replace Basic. The 6128 has internal ROMs 0 and 7 (0 can be overwritten but not 7). In German CPC6128 both, 0 and 7, can be overwritten. | ||
| + | The 6128plus series can overwrite both 0 and 7. | ||
| + | The Plus CPCs don't have internal ROMs, it was "out-sourced" to the Cartridge. The cartridge is actually situated in ROM positions 128 onwards, but the ASIC in the Plus re-maps the cartridge ROMs to 0 and 7 for compatibility. | ||
| − | + | == Lower ROMs == | |
| − | + | [[Image:FO.DOS Cartridge (photo from mic-cpcrulez).jpg|thumb|280px|right|FO-DOS - A Lower ROM expansion used to replace the internal Firmware]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | A further ROM is present inside the CPC. This Firmware ROM is in all CPCs, but is mapped to a different area of memory and also doesn't have a ROM Number. It's also possible to overwrite this ROM externally, however this can't be done with a standard ROMBoard, only with a Lower ROM expansion such as the [[FO-DOS|FO-DOS]] or the [[LowerROM|LowerROM Board]]. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Download ROMs == | |
| − | + | For detailed information and download links for the available ROMs, please refer to the [[ROM_List|ROM Software List]]. | |
| + | There are also specific pages on the wiki which relate to the available [[Plus System Cartridge|Plus System Cartridge]] ROMs and [[Amstrad/Schneider_Printer_Resources|Amstrad Printer]] ROMs. | ||
| − | [[Category:Expansion ROM]] | + | [[Category:Expansion ROM| ]][[Category:Software| ]][[Category:Hardware| ]][[Category:Operating System| ]][[Category:DATA Storage| ]][[Category:CPC Internal Components]] |
Latest revision as of 14:10, 26 December 2023
Contents
What Exactly are Internal and Expansion ROMs
The CPC hardware is designed to (theoretically) take up to 256 external ROMs, each ROM can be up to 16K and are numbered starting from 0. Each ROM can contain one or more programs or utilities. These ROMs are known as Upper ROMs and sometimes referred to as sideways ROMs. The programs are started using an "RSX" command: ie: A command with the bar "|" in front - eg: the command |M is used to to start Maxam. Standard ROMBoards such as the Rombo ROMBox or modern solutions such as Inicrons ROM-RAM-Box or the MegaFlash allow you to attach and use these ROM programs on a CPC. Older ROMBoards usually only supported 6 or 8 ROMs and each ROM was an individual EPROM chip. Whereas modern versions (SF2, ROM-RAM-Box, Ram7s RamCard, MegaROM, MegaFlash) support up to 32 ROMs and have combined several virtual ROMs within a single larger chip.
Many programs and utilities were released on ROM for three good reasons:
- They start instantly, because they don't actually need to be loaded.
- They are always present in the background and can be called/started without needing to insert a disk or tape - Useful for utilities such as Basic extensions or Disc utilities.
- They usually run directly from the ROM, not from RAM, so the RAM is still 99.9% empty - Useful for text editors and compilers because the RAM is free to be used for data.
No games were ever released on ROM, probably due to the 16K size limit and the fact that very few CPC users owned a ROMBoard.
The Hardware
The CPC can choose which ROM chip is associated with the 16K area starting at &C000. This is usually the reserved for the contents of the screen (RAM), but the address range is shared with ROM Memory.
On start up, the CPC checks whether any ROMs are installed using the "KL_ROM_WALK" firmware routine. The CPC464 only checks for ROMs in positions 7-0, but the 6128 checks for ROMs in positions 15-0. The ROMs are scanned in the reverse order starting from 7 or 15 depending on the CPC type. If a ROM is present, the CPC reads what commands the ROM offers and saves them in a table in RAM.
Further detailed information on the ROM bank numbering can be found here
A full list of all ROMBoards available for the CPC can be found here
The plans for many DIY ROMBoards can also be found here
Reserved ROM Numbers
There are two special ROM positions: ROM 0 is reserved for Basic (known as a type &80 ROM - Foreground ROM) and ROM 7 is reserved for the Disc Operating System - Not present on a 464, AMSDOS on a 6128. The CPC464 has one internal upper ROM (ROM 0) which can be overwritten by a ROMBoard to replace Basic. The 6128 has internal ROMs 0 and 7 (0 can be overwritten but not 7). In German CPC6128 both, 0 and 7, can be overwritten. The 6128plus series can overwrite both 0 and 7. The Plus CPCs don't have internal ROMs, it was "out-sourced" to the Cartridge. The cartridge is actually situated in ROM positions 128 onwards, but the ASIC in the Plus re-maps the cartridge ROMs to 0 and 7 for compatibility.
Lower ROMs
A further ROM is present inside the CPC. This Firmware ROM is in all CPCs, but is mapped to a different area of memory and also doesn't have a ROM Number. It's also possible to overwrite this ROM externally, however this can't be done with a standard ROMBoard, only with a Lower ROM expansion such as the FO-DOS or the LowerROM Board.
Download ROMs
For detailed information and download links for the available ROMs, please refer to the ROM Software List.
There are also specific pages on the wiki which relate to the available Plus System Cartridge ROMs and Amstrad Printer ROMs.