Technical
- Uses a 16KB ROM paged into memory at &0000.
- Uses a 8KB static RAM paged into memory at &c000-&dfff and repeats again at &e000-&ffff.
- ROM is paged into the range &0000-&3fff when the red button is pressed and the NMI vector is executed.
- When the black button is pressed, the ROM is paged into the range &0000-&3fff and executes it at &0000.
- This checks the BASIC ROM version, and clears the extra ram if a BASIC ROM from a CPC6128 is found.
Code:
0000 f3 di ;; disable maskable interrupts 0001 0100df ld bc,0df00h ;; select upper rom 0 0004 ed49 out (c),c 0006 01817f ld bc,7f81h ;; enable upper rom (mode 1 too) 0009 ed49 out (c),c 000b 31febf ld sp,0bffeh ;; setup stack which is not initialised after reset 000e 3a02c0 ld a,(0c002h) ;; read BASIC ROM version number 0011 fe02 cp 02h ;; CPC6128? 0013 cc2e0c call z,0c2eh ;; erase extra RAM ;; this appears to set it up for a reset.. 0016 210000 ld hl,0000h 0019 e5 push hl 001a e5 push hl 001b c30038 jp 3800h ;; I think the hardware monitors for address 3800h and if found disables the ROM
- Uses NMI
- Doesn't capture the hardware state like the Multiface does. Code in the ROM reads the hardware state which it restores when resuming the program.
- RAMDIS is asserted when ROM or RAM are active meaning no write through to ram behind.
- Menu code is at offset &3810 and is copied into RAM at &A200.
- Uses port FBF0 (write only)
FBF0 decoding is: 1111 1011 1111 00xx
FBF0 output: bit 0 is ram enable/disable state bit 1 is rom enable/disable state bit 2 is A10 on RAM bit 3 is A11 on RAM bit 4 is A12 on RAM bits 5-7 are not used.
- Uses port FBFF (input).
bit 7 is used - not sure for what.
Decoding of FBFF is:
1111 1011 1111 11xx
- The same plastic case is used by the Spectrum version of this interface.
- The spectrum has two switches on the top. One of which chooses load/save.
- In the Amstrad these holes are filled with plastic caps.
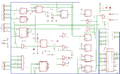
Pictures
- Transtape
- Transtape Layout, thanks to Jose Leandro
Manual
Downloads
- Transtape-ROM.zip (Transtape ROM)
- Transtape (eagle).zip (Transtape files for Eagle)