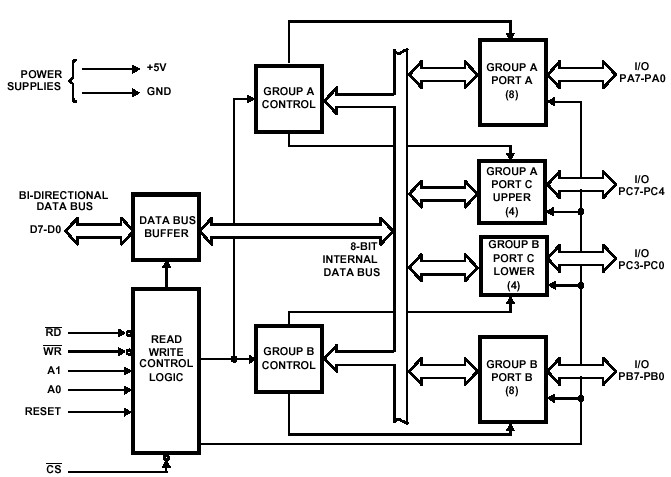
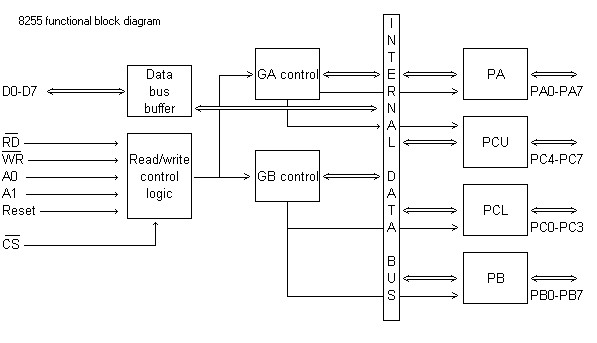
The 8255 in the CPC
The 8255 PPI chip is a general purpose input/output IC. This document will describe it's role in the Amstrad CPC,CPC+ and KC compact systems. To understand it's full functions please read the datasheet.
In these systems it is connected to the AY-3-8912 Programmable Sound Generator (PSG), keyboard, cassette recorder, the VSYNC of the 6845 CRTC and the "busy" signal from the parallel port.
The PPI is selected when A11 of the I/O port address is set to "0", A9 and A8 then define the PPI function access (as shown below), A15-A12 and A10 should be "1" (to prevent conflicts with other hardware), A7-A0 are don't care. So, resulting Port addresses are:
| I/O address | A9 | A8 | Description | Read/Write status | Used Direction | Used for |
| &F4xx | 0 | 0 | Port A Data | Read/Write | In/Out | PSG (Sound/Keyboard/Joystick) |
| &F5xx | 0 | 1 | Port B Data | Read/Write | In | Vsync/Jumpers/PrinterBusy/CasIn/Exp |
| &F6xx | 1 | 0 | Port C Data | Read/Write | Out | KeybRow/CasOut/PSG |
| &F7xx | 1 | 1 | Control | Write Only | Out | Control |
In the CPC+, the 8255 is integrated into the ASIC. The "emulation" is not complete and some functionality is not available. Please see the "Extra CPC+ documentation" for more information.
- Mode 1 (Strobed Input/Output) and Mode 2 (Bi-Directional Bus), as far as I know, are not used by any program, Mode 0 (Basic Input/Output) is always used.
Port Usage
- NOTE - If you are using the firmware, always return the operating modes and I/O state of the ports used to their settings below. The firmware expects the settings to be the same as given below and may operate incorrectly if they are not.
PPI Port A
Operating system settings:
- I/O Mode 0,
- For writing data to PSG all bits must be set to output,
- for reading data from PSG all bits must be set to input (thereafter, output direction should be restored, for compatibility with the BIOS).
| Bit | Description | Usage |
| 7-0 | PSG.DATA | PSG Databus (Sound/Keyboard/Joystick) |
PPI Port B
Operating system settings:
- I/O Mode 0,
- Input
| Bit | Description | Usage in CPC | Usage in KC Compact |
| 7 | CAS.IN | Cassette data input | Same as on CPC |
| 6 | PRN.BUSY | Parallel/Printer port ready signal, "1" = not ready, "0" = Ready | Same as on CPC |
| 5 | /EXP | Expansion Port /EXP pin | Same as on CPC |
| 4 | LK4 | Screen Refresh Rate ("1"=50Hz, "0"=60Hz) | Set to "1"=50Hz (but ignored by the KC BIOS, which always uses 50Hz even if LK4 is changed) |
| 3 | LK3 | 3bit Distributor ID. Usually set to 4=Awa, 5=Schneider, or 7=Amstrad, see LK-selectable Brand Names for details. | Purpose unknown (set to "1") |
| 2 | LK2 | Purpose unknown (set to "0") | |
| 1 | LK1 | Expansion Port /TEST pin | |
| 0 | CRTC VSYNC | Vertical Sync ("1"=VSYNC active, "0"=VSYNC inactive) | Same as on CPC |
- LK1-4 are links on the mainboard ("0" bits are wired to GND). On CPC464,CPC664,CPC6128 and GX4000 they are labeled LK1-LK4, on the CPC464+ and CPC6128+ they are labeled LK101-LK103 (and LK104, presumably?).
- Bit5 (/EXP) can be used by a expansion device to report it's presence. "1" = device connected, "0" = device not connected. This is not always used by all expansion devices. is it used by any expansions? [in the DDI-1 disc interface, /EXP connects to the ROM bank selection, bank 0 or bank 7]
- For more info on LK1-LK4 (and further LKs) see LK Links
PPI Port C
Operating system settings:
- upper: I/O Mode 0, lower: I/O mode 0,
- upper: output, lower: output
| Bit | Description | Usage |
| 7 | PSG BDIR | PSG function selection |
| 6 | PSG BC1 | |
| 5 | Cassette Write data | Cassette Out (sometimes also used as Printer Bit7, see 8bit Printer Ports) |
| 4 | Cassette Motor Control | set bit to "1" for motor on, or "0" for motor off |
| 3 | Keyboard line | Select keyboard line to be scanned (0-15) |
| 2 | ||
| 1 | ||
| 0 |
PSG function selection:
| Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Function |
| 0 | 0 | Inactive |
| 0 | 1 | Read from selected PSG register |
| 1 | 0 | Write to selected PSG register |
| 1 | 1 | Select PSG register |
PPI Control
This register has two different functions depending on bit7 of the data written to this register.
PPI Control with Bit7=1
If Bit 7 is "1" then the other bits will initialize Port A-B as Input or Output:
Bit 0 IO-Cl Direction for Port C, lower bits (always 0=Output in CPC) Bit 1 IO-B Direction for Port B (always 1=Input in CPC) Bit 2 MS0 Mode for Port B and Port Cl (always zero in CPC) Bit 3 IO-Ch Direction for Port C, upper bits (always 0=Output in CPC) Bit 4 IO-A Direction for Port A (0=Output, 1=Input) Bit 5,6 MS0,MS1 Mode for Port A and Port Ch (always zero in CPC) Bit 7 SF Must be "1" to setup the above bits
- CAUTION: Writing to PIO Control Register (with Bit7 set), automatically resets PIO Ports A,B,C to 00h each!
- In the CPC only Bit 4 is of interest, all other bits are always having the same value. In order to write to the PSG sound registers, a value of 82h must be written to this register. In order to read from the keyboard (through PSG register 0Eh), a value of 92h must be written to this register.
PPI Control with Bit7=0
Otherwise, if Bit 7 is "0" then the register is used to set or clear a single bit in Port C:
Bit 0 B New value for the specified bit (0=Clear, 1=Set) Bit 1-3 N0,N1,N2 Specifies the number of a bit (0-7) in Port C Bit 4-6 - Not Used Bit 7 SF Must be "0" in this case
Programming Examples
1. Using the control byte
- Setting bit 7 of port C to 1,
LD B,&F7 ;8255 Control port
LD A,%00001111 ;Bit Set/reset function
OUT (C),A ;Send it to 8255
RET
- Set port A to input, operating in mode 0, port B to output, operating in mode 0 and port C to input, operating in mode 0.
LD B,&F7 ;8255 Control port
LD A,%10011001 ;Configuration function
OUT (C),A ;Send it to 8255
RET
2. Using port A/B/C,
In this example, port A is set to output, port B is set to input, and port C is set to output, and they are all operating in mode 0.
We will only be using port A for these examples.
- Reading from port A,
;Set port A to input
LD B,&F7 ;8255 Control port
LD A,%10010010 ;Configuration function
OUT (C),A ;Send to 8255
LD B,&F4 ;Port A port address
IN E,(C) ;Get byte from port
;Register E holds value from port
;Return port I/O status and operating modes
;to previous settings.
LD B,&F7 ;8255 Control port
LD A,%10000010 ;Configuration function
OUT (C),A ;Send to 8255
RET
- Writing to port A,
;Set port A to output
;(Note the next few lines are not necessary
;as port A is already acting as output, however
;it is given here just to make the example
;more understandable)
LD B,&F7 ;8255 Control port
LD A,%10000010 ;Configuration function
OUT (C),A ;Send to 8255
LD B,&F4 ;port A port address
;Register E holds value to put into port
LD E,&FF ;Data to put into port
OUT (C),A ;Send to port A
;Return port I/O status and operating modes
;to previous settings.
LD B,&F7 ;8255 Control port
LD A,%10000010 ;Configuration function
OUT (C),A
RET
Diagrams
Resources
- Media:PPI M5L8255AP-5.pdf PPI Datasheet (Mitsubishi)
- VHDL implementation of the 8255 PIO