Description
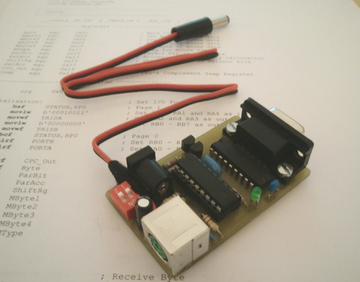
The following project describes how to construct an AMX compatible PS/2 and USB Mouse adapter for the Amstrad CPC. I’ve never actually owned an AMX Mouse, in fact I’ve never even seen one other than in pictures. Back in the 80s I had no need for one, but with GUIs like FutureOS and SymbOS now available, I decided it was time to get my own…or at least build an equivalent. Like other projects that I’ve shared in the community, I’ve tried to keep this project as simple as possible to construct and as cheap as possible to build, otherwise it scares people from trying to build it for themselves. That said, you will need to be proficient at soldering and possibly need to produce your own PCB, if you wish for your end product to look like the one above. I have also supplied a single sided layout, to make it easier for those of us who like to produce our own PCBs. While designing the circuit, I realised that most modern mice have a scroll wheel which wasn’t available back then on the AMX. As the CPC has a few inputs spare on the port (Joy2), I decided to make them accessible by binding them to the Joy2 up and down signals. Although this isn’t strictly AMX compatible, I thought the people at SymbOS or FutureOS, might like to take advantage of them, so consider this adapter is AMX+ compatible.
Warning / Disclaimer
Although I have taken the utmost care preparing this documentation, I do not guarantee that it is error free and I accept no responsibility for damage to anyone’s CPC, Mouse or other personal equipment or injury inflicted on you or others.
The Circuit
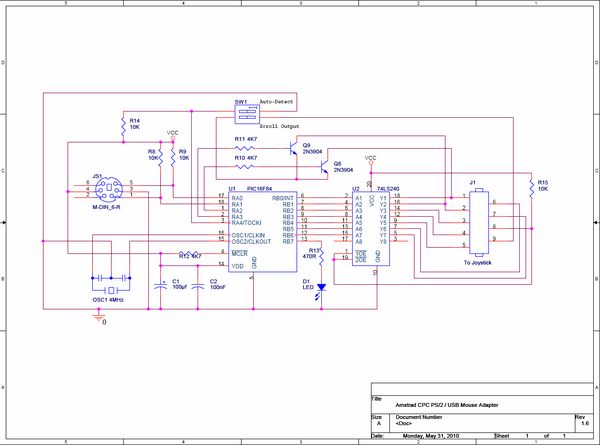
The main component on the board is the PIC16F84A. This is a small micro-processor which is pretty much dumb without some firmware to tell it what to do, I will go further into detail about the firmware below. The processor is running at 4 MHz, so the low cost version is all that’s required (there’s a slightly more expensive version which can go up to 20Mhz which would also work). I have used a 4 MHz resonator to save space. The other chip seen above is the 74LS240. This is a TTL buffer chip which is triggered by the CPC each time the Amstrad polls the joystick port, this eases the µPs job, because it doesn’t need to watch what the CPCs up to. The two transistors are used to trigger the Scroll-wheel inputs.
The PIC has two configurable ports RA and RB. In this circuit RB is configured as all outputs, seven of them are used to control the signals to the CPC, while the eight controls the LED. RA has only 5 pins, but it is a little more complicated, the first two pins are connected to the Clock and Data line of the mouse port, these change direction permanently from inputs to outputs, depending on which way the communications are going (yes, the mouse needs to get info too). The next two are always outputs and control the scroll wheel signals to the CPC. The last pin is an input connected to one of the small red dip-switches, which can be used to make a setting in the PIC, but more on that later.
Parts List
As I mentioned above, one of my priorities is always to keep the price as low as possible, and according to my local supplier, the cost of the entire board should come in at under 8€. Here’s the Parts list and their approximate prices:
| Component | Quantity | Price | Total |
| PIC16F84A-04P | 1 | 2.40 | 2.40 |
| 4 MHz Ceramic Resonator | 1 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 74LS240 | 1 | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| 2N3904 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.08 |
| 100µf 16V Electrolytic Capacitor | 1 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 100nf Ceramic Capacitor | 1 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 10K 1/4W Resistor | 3 | 0.05 | 0.15 |
| 4K7 1/4W Resistor | 3 | 0.05 | 0.15 |
| 470ohm 1/4W Resistor | 1 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 3mm LED Green | 1 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| 18 Pole IC Socket | 1 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 20 Pole IC Socket | 1 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 9 Pole D-Sub Connector 90° | 1 | 0.24 | 0.24 |
| 6 Pole Mini DIN Socket | 1 | 0.53 | 0.53 |
| 2 Pole DIP Switch | 1 | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| 5V Power Socket | 1 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| 5V Power Plug | 1 | 0.58 | 0.58 |
| 160x100x1.5mm 35µ Single Sided photo-resist PCB | 1 | 1.70 | 1.70 |
The Firmware
The firmware is written in PIC assembler. Its more or less a PS/2 driver with a little bit added to convert every movement into signals the Amstrad can work with, its first job is to get the mouse to life, it sends the required initialisation sequence and sets up some variables available in the mouse. Among other things, I have slightly de-sensitised the mouse, so that a single twitch doesn’t send the arrow shooting across the screen. As well as this, it checks whether the mouse has a scroll wheel and turns it on if it does. After that, it just continuously asks the mouse if it has moved and collects the data the mouse sends back, this is then converted into the corresponding up/down/left/right and fire inputs that the CPC needs. I haven’t published the source code here, but if anyone is interested, I may be willing to share it for educational purposes.
Installing the Firmware
I have supplied a pre-compiled HEX file, so you don’t have to worry about installing additional assemblers or having to compile things yourself. You will however need to get the program onto the chip. If you don’t know how to program a PIC, I would suggest you do some research on the JDM programmer, an even smaller PCB that allows you to program the chip through an RS232 port using freeware software such as PikLab if you’re a Linux user or ICProg if windows is your preferred PC OS. A quick warning: I'm told that the JDM doesn't work on Laptop Com-ports because they don't supply the required 12V, so keep this in mind if you build one. The total price to build a JDM programmer should be under 2€.
Construction Tips
As with the original AMX Mouse, the only connections needed to the CPC are through the joystick port and to the 5V supply. I have kept the PCB size to a minimum, to allow the board to be connected directly to the joystick port without getting in the way too much or tearing the connector off the side. You may choose an alternative layout to mine, but remember that if it is too large, it may damage the joystick port and would be better with a fly-lead connection. The board presented here measures just 38mm x 60mm and should cause absolutely no stress to the CPCs connector. As well as that, remember that there are connectors left and right of the joystick port that you might want to use simultaneously, the layout here has been designed to keep both the sound socket and tape port free.
A note to beginners: When soldering the parts to the board, always solder the most heat resistant parts first and leave the sensitive ones to last, this avoids destroying a successfully soldered transistor while trying to solder a resistor that’s right beside it. Also, although you may notice that I have soldered the 74LS240 into place, I wouldn’t advise beginners to try this, you will destroy it. Splash out on the extra 7 cents it costs for a suitable socket. If you’re an absolute beginner, there are even sockets available for transistors, but the spacing on this layout probably isn’t correct for them. Also remember that there are wire bridges under each of the ICs! These are really difficult to assemble, if the socket is there already!
The 9 way Sub-D connector used usually has two small bolts protruding left and right of the connector, if you remove these, the metal surround will fall off. I used some superglue to re-attach the metal part. It will work without the metal surround, but this will cause the circuit to bend the CPCs joystick pins over time, so I would recommend you do the same. I also added to M3 screws to hold the Sub-D connector to the PCB, this takes the stress off the pins below the connector, which could develop cracks in the solder over time as well.
Using The Mouse
There are two switches on the PCB, the inner one (beside the power socket), allows the user to choose whether a scroll mouse is being used or not. In the ON position the PIC will try to initialise a scroll wheel mouse, if the mouse has no scroll wheel an error will occur. In the OFF position a non scroll-wheel mouse will be assumed, this setting should work with all mice, even if they have a scroll wheel, but the scroll function will be ignored. This switch needs to be set before power is applied. The second switch allows you to pass the scroll wheel movements on to the CPC, when both switches are ON, movement to the scroll-wheel will cause a “5” for each roll upwards and a “6” for each scroll downwards, this may have negative effects with software which has assigned these characters to other functions, so the switch allows you to block the messages, this switch can be used at any time without resetting.
Before connecting power to the PCB the mouse needs to be connected and the PCB should already be connected to the joystick port. The mouse is not Plug & Play, so disconnecting the mouse will mean having to restart the Amstrad (because you need to pull the 5V power plug to reset). The 5V power lead that usually goes to the CPC should be connected directly to the Adapter PCB, the fly-lead is then plugged into the CPC. When the power is applied, the PIC will try to initialise the mouse. If it is successful, the LED will blink once. After this any movement of the mouse will make the LED blink. If the mouse fails to initialise (there may be incompatible ones out there or it may just be broken) the LED will flash continuously in one second intervals. This error signal also occurs if the inner switch is ON, but the mouse has no scroll wheel.
Testing The Mouse
In Basic, moving the mouse should produce the arrows usually seen when a joystick is connected. Pressing the left button will produce an X and the right button produces a Z. The centre button will not show any visual feedback in Basic, but can be sensed using the Inkey(78) command.
Compatibility
Like I mentioned above, I’ve never seen an AMX mouse, so I don’t know exactly how they react to movement, how fast they were or how they “felt”. Technically speaking, the mouse adapter described here is fully AMX compatible and works perfectly with AMX compatible packages. I have tuned the feel of the mouse to closely resemble a PC mouse, but if you build this and find that it’s not quite the “AMX feel”, let me know and I might be able to tune it back to the 80s.
The adapter should work with any PS/2 compatible mouse and almost any USB mouse using a USB to PS/2 adapter plug. If you have a fancy 28 Button Star-Fighter special edition all singing and dancing cyber mouse, then leave both switches in the OFF position and it should still work by being forced into ID 00 Mode (Basic mouse mode).
Bluetooth USB mice will NOT work with this adapter.
I have tested the hardware with the following mice:
(Many thanks to my good friend Knut, who was kind enough to lend me varied mice from his enormous "All things x86" collection)
Yes that’s a wireless PS/2 mouse on the right. (Is that the first wireless CPC mouse ever? Who knows.)
Resources
File:PS2Mouse Layout.pdf - PCB Track Layout
File:PS2Mouse Components.pdf - PCB Component Layout
File:PS2Mouse V09.HEX - Firmware V0.9
Further Info
The software is still in its Beta stage, there will be further versions offering more compatibility and functions including Plug & Play when I have time, but the hardware will not change.
If you have any further questions regarding this project, please contact me through the Wiki Forum.
Bryce.