(→Technical specs: - added datasheet, formatting) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
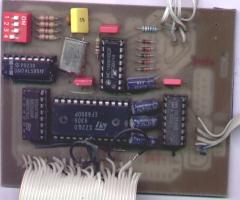
| − | [[Image:CPCAI-RS232interface.jpg|thumb|[[Octoate|Octoate's]] | + | [[Image:CPCAI-RS232interface.jpg|thumb|[[Octoate|Octoate's]] self-built version of the CPCI RS232 interface]] |
| − | This [[RS232]] interface was published as a DIY project in a special edition of the the German | + | This [[RS232]] interface was published as a DIY project in a special edition of the the German magazine: [[CPC Schneider International Sonderheft]] (#3-1986) and also in a later issue. |
| − | magazine: [[CPC Schneider International]] ( | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
As the standard CPC series does not include a [[RS232]], this interface was very handy in order to communicate with other computers(eg. IBM PCs). A major drawback was the missing interrupt line which means that your programs have to poll the interface. | As the standard CPC series does not include a [[RS232]], this interface was very handy in order to communicate with other computers(eg. IBM PCs). A major drawback was the missing interrupt line which means that your programs have to poll the interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Software == | ||
| + | |||
| + | A terminal program, written by [[The Cranium]], for this serial interface was published in the last issue of the [[CPC Schneider International]] (12/1 1992/1993). | ||
== Technical specs == | == Technical specs == | ||
| − | + | Contains a single 25pin DSUB connector, a MC6850 chip (ACIA), MAX 232 voltage converter, 74LS138 and 74LS85 address decoders, and a 4MHz oscillator with HEF 4060 clock divider, the clock divider connects to a mechanic switch, allowing to select between 19.2kHz and 38.4kHz. Four dip-switches allow to select the port addresses (FxDCh and FxDDh, with x=0..F, usually x=8). | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | F8DCh CPCI Serial Interface MC6850 Control/Status Register (R/W) | |
| − | + | F8DDh CPCI Serial Interface MC6850 Data Register (R/W) | |
| + | |||
| + | * [[6850 ACIA chip]] | ||
* [[Media:MC6850.pdf|Motorola MC6850 datasheet]] | * [[Media:MC6850.pdf|Motorola MC6850 datasheet]] | ||
| + | * [[Media:Max232.pdf|MAX232 datasheet]] | ||
== How to build a RS232 interface (German) == | == How to build a RS232 interface (German) == | ||
| Line 26: | Line 30: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Peripherals]] [[Category:Serial interfaces]] [[Category:Communication Software]] [[Category:DIY]] |
Latest revision as of 08:00, 10 March 2018
This RS232 interface was published as a DIY project in a special edition of the the German magazine: CPC Schneider International Sonderheft (#3-1986) and also in a later issue.
As the standard CPC series does not include a RS232, this interface was very handy in order to communicate with other computers(eg. IBM PCs). A major drawback was the missing interrupt line which means that your programs have to poll the interface.
Software
A terminal program, written by The Cranium, for this serial interface was published in the last issue of the CPC Schneider International (12/1 1992/1993).
Technical specs
Contains a single 25pin DSUB connector, a MC6850 chip (ACIA), MAX 232 voltage converter, 74LS138 and 74LS85 address decoders, and a 4MHz oscillator with HEF 4060 clock divider, the clock divider connects to a mechanic switch, allowing to select between 19.2kHz and 38.4kHz. Four dip-switches allow to select the port addresses (FxDCh and FxDDh, with x=0..F, usually x=8).
F8DCh CPCI Serial Interface MC6850 Control/Status Register (R/W) F8DDh CPCI Serial Interface MC6850 Data Register (R/W)



